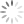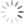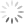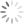Hidden in Plain Sight: LGBT+ Histories
By Sarah S Pipkin, on 23 June 2023
The following was adapted from text written by Erika Delbecque and Tabitha Tuckett for the 2023 exhibition catalogue Hidden in Plain Sight: Liberating our Library Collections. The Main Library exhibition Hidden in Plain Sight is open until December 2023 and is open to the public. For more information, visit UCL Library’s Exhibition page.
Since 2021, we’ve run the Liberating the Collections volunteer project. Volunteers search our catalogues for Rare Books related to marginalised voices, including examples of historical LGBT+ writers in our collections. The items identified by our volunteers illustrate diversity of sexuality and gender identities present in our collections, while also highlighting the difficulty of applying modern notions of LGBT+ identites to authors who predate them.
One example is Katherine Philips (1632-63). She was one of the first female poets whose work was published during her lifetime. We have several editions of her poetry in our collections, including the 1669 edition of Poems by the most deservedly admired Mrs Katherine Philips.

Author portrait from Poems by the most deservedly admired Mrs Katherine Philips, 1669.
Philips wrote vivid poems about friendships between women, interpreted by some critics as examples of lesbian poetry. One of her poems, “To my Lucasia, in defence of declared Friendship.” begins:

First page of “To my Lucasia”
1.
O My Lucasia, let us speak of our Love,
And think not that impertinent can be,
Which to us both doth such assurance prove,
And whence we find how justly we agree.
2.
Before we knew the treasures of our Love,
Our noble aims our joys did entertain;
And shall enjoyment nothing then improve?
‘Twere best for us then to begin again.
The debate on whether Philips’s work should be read as such points to the difficulty of applying modern notions of sexuality and sexual identity to historical authors.

Author portrait from A narrative of the life of Mrs Charlotte Charke.
Charlotte Charke (1713–60) lived and worked as a man for much of her life, defying some of the career limitations for women in eighteenth-century England. Her autobiography A narrative of the life of Mrs Charlotte Charke … Her adventures in men’s cloaths records her experiences. To contemporaries she was notorious, but her works in our collections have received little attention until recently.
We use she/her pronouns when describing her as those are the pronouns she used to describe herself.

Title page of Charke’s autobiography “Written by Herself”.
Charke acted on the stage in male roles, ran a puppet theatre staging political satire and worked in the traditionally male jobs of a gentleman’s valet and a farmer. Unfortunately she paid a price for doing so: frequently short of money, she was estranged from her father and two husbands, against whose affairs and gambling debts she rebelled. Only towards the end of her life, as a writer, did she find success with this book, an early example of a published autobiography written by a woman. We might be tempted to apply anachronistic terms of gender identity to Charke, but the survival of her autobiography at least enables us to read about her life in her own words.
During the eighteenth century, English guidebooks claiming to describe the dangerous temptations of London life to the innocent and respectable reader became popular. They enabled a vicarious exploration of illicit or unconventional sexual behaviour and gender that did not endanger either author or reader. The midnight spy … exhibiting .. bagnios, jelly houses .. and other places of midnight resort, focusing on London’s nightlife, includes an account of jelly houses and bagnios – restaurants and bathhouses that served as brothels where men could pick up both women and other men for sex, although the text does not clarify whether it describes homosexual or heterosexual activity.
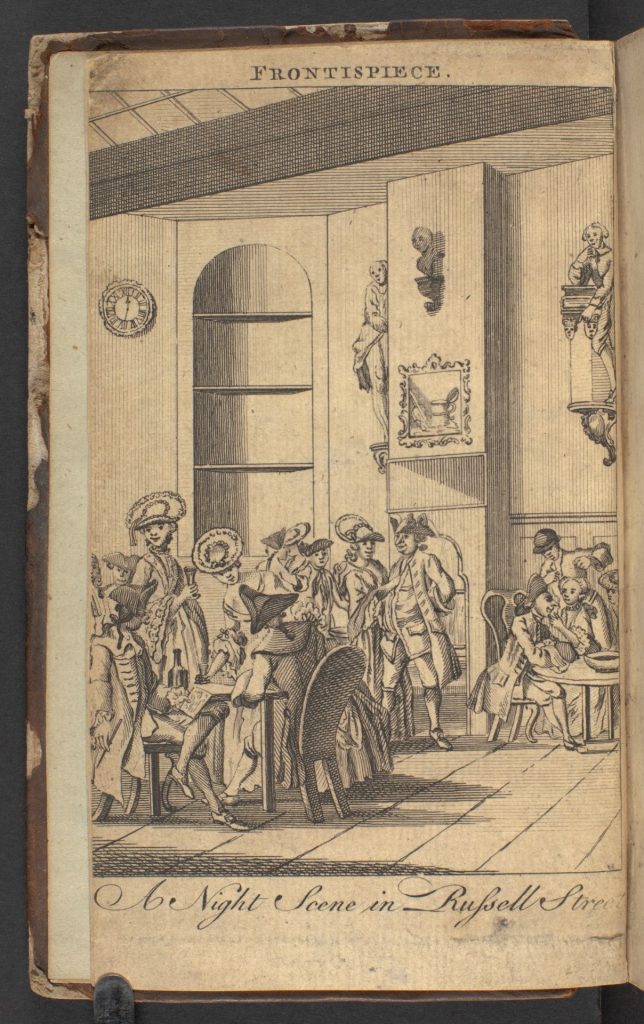

Frontispiece of The Midnight Spy
Publications of this sort sold well and critical reviews from 1766 mention that passages of this book had been re-used from previous similar titles. Such comments suggest that this may not have been the most up-to-date account of London nightlife during time of rapid change in the capital as the Industrial Revolution began.
These items were indentified by Isobel Goodman (2021 Liberating the Collections volunteer), Chris Fripp (Liberating the
Collections pilot-project researcher 2019–20), and Michael Niedzwiecki (2022 Liberating the Collections volunteer). Thanks to their work, we can highlight these items and ensure they are no longer hidden on our shelves and in our catalogue.
If you would like to see these items for yourself, they are on display in the Main Library until December 2023.
 Close
Close