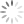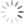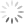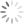Women in the Italian Book Trade: forgotten owners and producers of Italian books
By Erika Delbecque, on 23 August 2021
This guest blog post was written by Sara D’Amico, who spent six months volunteering at UCL Special Collections as part of the Liberating the Collections project
We might think that women were not allowed to participate in skilled crafts: for instance, the art of book binding was foreign to them until the nineteenth century. But women have always been involved in the book trade. However, many of them have remained in the shadows and their contribution has not been acknowledged for centuries. The Liberating the Collections project aims to fix this and give the women who are represented in the rare book collections at UCL Special Collections the recognition they deserve. As a volunteer in the LTC project, I have conducted a focused search among the Castiglione and Dante Collections, to allow the women involved in the Italian book trade to come to the fore. What follows is only a brief overview of some of the most interesting people involved in the making and keeping of Italian books.
Luchina Ravani (active ca. 1532-1541)

Luchina Ravani’s edition of “Il libro del cortegiano” (1538) [STRONG ROOM CASTIGLIONE 1538 (1)]
Sofia Giacomelli (1779-1819)

Sofia Giacomelli’s illustrations of the “Divina Commedia” (1813) [DANTE DD 5 K]
Also known as Sophie Janinet and Madame Chomel, Sofia was a popular singer and an accomplished graphic artist: she even exhibited her work at the Paris Salon in 1799 and in 1800. Art magazines from all over Europe praised her work in illustrating Milton’s Paradise Lost and Dante’s Divina Commedia. The Journal des arts, des sciences, et de littérature reviewed her Milton collection in 1813: “The collection of the twelve figures of Madame Giacomelli is one of the most agreeable productions that engraving has offered us for a long time. We live in a century when women have won the most distinguished rank in literature: it is enough to look at this work to discover that the field of the arts is not foreign to them either.” But most importantly, Sofia didn’t stop working on her engravings after her marriage in 1802 with musician Joseph Giacomelli, who introduced her in the world of music and singing. She was, first and foremost, an artist.

Sofia Giacomelli’s illustrations of the “Divina Commedia” (1813) [DANTE DD 5 K]
Caroline Morris (dead after 1870)
Caroline Morris was not an occasional book owner: together with her husband she formed a library of about 9,000 volumes, making her a book collector on all counts. In the nineteenth century it was not common for a woman to collect that many books and it was even less common for a woman with no titles and significant richness to do so. James Morris, Caroline’s husband, was a Professor of Languages in the Royal College of Mauritius and the UCL Calendar (1870-71) seems to suggest that he was the owner of this extensive and valuable library: apparently, he bequeathed it to his wife for the duration of her lifetime, and after her death to the College. And yet, the illustrated bookplates that can be found in the books clearly say: “Jacobus et Carolina Morris”.

Letter from J. M. Peebles to Caroline Morris. [MS ADD 133]
There are many women like Luchina, Sofia and Caroline who contributed to the making and preserving of some of the finest rare books in the UCL Special Collections. Their names are often overshadowed by those of their husbands but the LTC Project is finally giving them a new voice. While there is still room for more research, these first results are an indication of how many valuable resources are hidden within the UCL Special Collections and how much they can contribute to the study of the Italian book trade’s history.
References
Michelle Levy, ‘Do Women Have a Book History?’, in Studies in Romanticism, Vol. 53, No. 3 (2014), pp. 296-317.
Deborah Parker, ‘Women in the Book Trade in Italy, 1475-1620’, in Renaissance Quarterly, Vol. 49, No. 3 (1996), pp. 509-541.
Patricia Jeffe, Women Engravers, 1990.
Stephen S. Stratton, Woman in Relation to Musical Art, in Proceedings of the Musical Association, 9th Sess. (1882-1883), pp. 115-146.
 Close
Close