Understanding Research Metrics: UCL’s New LibGuide
By Rafael, on 29 May 2024
Guest post by Andrew Gray, UCL Bibliometrics Support Officer
The UCL Research Support team has recently launched a comprehensive new LibGuide on Research Metrics. This resource covers a range of topics, from how to use and understand bibliometrics (citation metrics and altmetrics) to guidance on specific tools and advice on handling publications data. Learn more about this guide to enhance your research impact and better understand the world of research metrics!

Image by Calvinius (own work), CC BY-SA 3.0
Bibliometrics
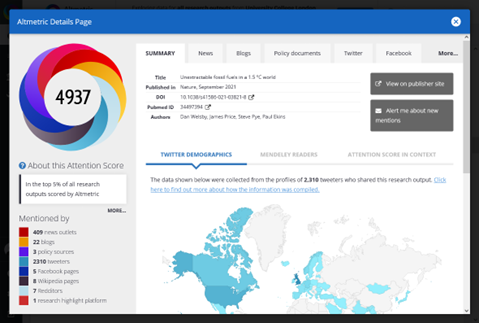
The core of the new guide is focusing on guidance for using and understanding research metrics, such as bibliometrics, citation metrics, and altmetrics. It explains how to access citation counts through Scopus and Web of Science, and more complex normalised metrics through InCites. It also gives guidance on how to best interpret and understand those metrics, and advice on metrics to avoid using. The guide also covers the UCL Bibliometrics Policy, which governs the use of bibliometric data for internal assessments at UCL, and sets some limits on what should be used.
Guidance for Tools
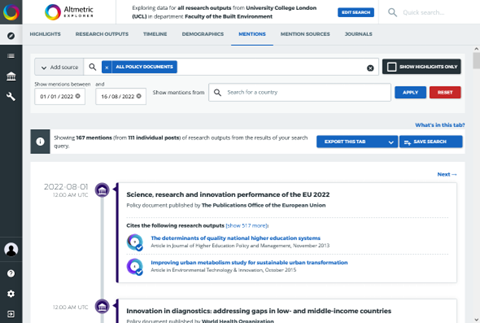
Within the LibGuide, you will also find guidance pages for how to use specialised services like InCites, Altmetric, and Overton to measure research impact. Additionally, the guide offers advice on using other tools that UCL does not subscribe to but may be beneficial for research support. This includes three freely available large bibliographic databases—Lens, Dimensions, and OpenAlex—which provide broader coverage than Web of Science and Scopus. It also outlines how to use a range of tools for citation-network based searching like Research Rabbit, Connected Papers, and Litmaps, as well as modern AI-supported search and summarising tools such as Scite, Keenious, and Consensus.
These are of course not the only tools available – especially with AI-supported tools, there are frequently tools being released – but these are ones we have been asked to investigate by students and researchers. If you would like feedback on another tool you are considering using, please get in touch.
Publications data
The LibGuide also addresses broader questions about using publications data. It outlines how to download publication and metrics datasets from Web of Science, Scopus, InCites, and Altmetric, and gives some guidance on how to link datasets from different sources together. Learn more about using publications data.
Additionally, the guide also explains how best to interpret data drawn from UCL-specific sources such as RPS, data ensuring you can make the most of the data available to you.
This new LibGuide is an important resource for anyone looking to expand their understanding of research metrics and manage their publications data. Visit the guide today to explore these tools and resources in detail.
Further support
We offer regular online or in-person training sessions as part of the Library Skills program. Please see the Library Skills calendar for dates and bookings. There are also three self-paced online sessions available through the Library Skills Moodle.
For any enquiries about bibliometrics, please contact us on bibliometrics@ucl.ac.uk
Get involved!
 The UCL Office for Open Science and Scholarship invites you to contribute to the open science and scholarship movement. Stay connected for updates, events, and opportunities. Follow us on X, formerly Twitter, LinkedIn, and join our mailing list to be part of the conversation!
The UCL Office for Open Science and Scholarship invites you to contribute to the open science and scholarship movement. Stay connected for updates, events, and opportunities. Follow us on X, formerly Twitter, LinkedIn, and join our mailing list to be part of the conversation!
 Close
Close