The ‘Slow Violence’ of Inaction: On the Apathy towards Air Pollution
By ucsawat, on 28 March 2016
Gansukh is 54 and has lived on his 25x25m plot with his family for the last 16 years. He and his wife are contractors for housing repairs—he is apparently very handy with a hammer—but the struggling economy has meant that his skills aren’t called on much these days. Two houses stand on his plot watched by his faithful German shepherd mix—one house where his two grown daughters, twins, live with their families, and the house he now occupies with his wife and youngest daughter (3-years-old). When I ask him about the air pollution, all he can do is sigh in resignation and complain about the coal: he hates shovelling coal, he says, it makes the entire house dirty, it covers your clothes, and fills the house and outside air with thick smoke. After a few hours, the smoke settles and falls on the ground, polluting the nearby soil and making it impossible to grow plants on their plot. The pollution is horrible, he repeats, but they need the heat.
Every morning, Gansukh and his wife join the over 200 thousand families (http://www.ikon.mn/n/nzn) living on the outskirts of UB that are dependent on coal to heat their domiciles. The day starts at 6am, when families light the first fire in order to warm up for the day ahead. The smoke then escalates until around 11, at which point it subsides until 5 pm while the sun is up. Then, as the day ends and families return home, the smoke re-emerges for dinner and apexes around midnight. This constant haze has hung over the ger districts—the sprawling underserved, infrastructure-lacking districts on the outskirts of Ulaanbaatar—the last winter months from November until March. Yet, despite the poor air quality and lack of access to reliable electricity and running water, these districts expand with every passing year—climaxing this year due to a struggling economy and extreme cold.

The state of my indoor Smart Air Filter (http://smartairfilters.com/en) after about a month of usage between January and February 2016. This was in the south of the city, away from the worst of the air pollution.
Flight to the Ger Districts
In contrast to the inner city, the largely unregulated, haphazard ger districts of Ulaanbaatar offer affordable refuge for newcomers from the countryside. Because of the tanking economy (mentioned extensively in previous posts) and extreme winters, unemployment in Mongolia’s countryside is high, and families increasingly move into the city in search of a better life and to send their children to school. The average land plot in the ger district is currently worth between 20,000,000 and 50,000,000 MNT (around 10—25,000 USD), which is much more affordable than flats—the average studio flat costs upwards from 60,000,000 MNT (30,000 USD), where a size-comparable flat would cost over 100,000,000 MNT (50,000 USD). Instead, unemployed newcomers often opt to live with families or rent space in the more reasonable ger districts. In addition, many former herders and countryside residents lack urban education and professionalization skills, making it difficult for them to find good paying jobs in the city. Thus, as jobs become scarce, ger districts families are increasingly dependent on the income of one family member and/or loans.
For example, Odnoo is a masseuse (57) and lives in the ger district with her husband (unemployed) and two sons—a student (19) and an unemployed driver (30). Odnoo originally came from Hentii 10 years ago, and bought her ger district plot for 900,000 MNT (around 439 USD) at the time. Her family lives off of her income, as the only working member of the family, and she makes around 400,000 (195 USD) a month. However, she has spent over 600,000 (291 USD) in the last five months on coal to heat her family, which means that over one fourth of her salary every month goes to heat. Other families, like the aforementioned Gansukh, are unemployed, but still manage to gather the 60,000 to 150,000 MNT (30-73 USD) a month (in a country where the minimum wage is 192,000 MNT [93 USD]) to pay for heat. Thus, the low start-up cost to move into the ger district, yet the high upkeep cost of maintaining a decent living standard mean that many poor and newcomer families get either locked into the ger district for years, or are severely limited in their lifestyle choices. And thus, with each passing year, the smoke on the urban landscape thickens with the mass of families.
Ulaanbaatar’s Reaction to Noxious Pollution
Because the smoke is the manifestation of the search for heat, many families react to the air pollution with various shades of apathy. Unlike other ‘disasters’, the smoke didn’t pop up overnight, but has slowly creeped up on residents from year to year, allowing locals to ‘gradually get used to it’ (Баг багаар дассан). Several years ago, the government and development bodies advocated the sale and usage of ‘improved stoves’ with ‘compressed wood’ that was received well by residents. But with time, these stoves have cracked and the companies that produce them haven’t been able to keep up with the demand as more and more families move into the ger districts. As one resident said resignedly, as long as we have stoves, we will have smog, meaning a more drastic improvement is required.
Gansukh, for example, knows that the smog is affecting his family. The local children, including his 3-year-old daughter, have a chronic cough, and instead of giving them cough medicine (like in the past) they now give their children allergy medicine. Several local families have had stillbirths and/or have miscarried because the baby stopped growing in the womb.[1] But locals can’t really do anything (юу ч хийж чадахгүй) but get used to it and wear scarves when outside over their nostrils. As for masks, Gansukh would wear them if he knew where to get them, but reasoned that they were probably too expensive. Thus, due to lack of capital (to buy e.g. solar panels) and dearth of alternatives (inability to find masks; the high costs of the inadequate electricity grid) burning coal continues to be the only reliable alternative to heating their homes in extreme temperatures.
Thus, Gansukh and other residents view the subject of ‘impenetrable smoke’ (битүү утаа) with ‘disinterest’ (тоохгүй). Odnoo mentioned that although she logically knew the smog was poisoning her (хордуулах), she couldn’t pin down its effects directly on her health. To her, the consequences were currently ‘imperceptible’ (мэдэгдэхгүй), allowing her to ignore the smog in the interim. Furthermore, the waves of smoke ebb and flow with the heat of the sun and the daily temperature—making the smoke seem almost like a natural phenomenon, another factor of the weather. Thus, in addition to common seasonal greetings like ‘are you cold?’, I had become accustomed to hearing ‘how is the smog?’ during the winter months. The abstract nature of the smog, both visually and perceptively as manifested in physical health, offers the potential of salvation—the possibility that one might remain unscathed and unaffected with time. Thus, ger district residents (who perceive no solution in their own immediate power) prefer to acclimate themselves to the risk that the smoke embodies around them and naturalize it as a feature of the weather and of urban life.
‘Slow Violence’ as Silent Killer
Although anthropologists have long used the term ‘structural violence’ to describe the disadvantaged social position of the poor, the air pollution in Ulaanbaatar could be better labelled what the scholar, Rob Nixon, calls ‘slow violence’. The term ‘violence’ conjures images of direct, instantaneous bodily harm. Yet, although the pollution is epidemic and causes long-term pain and death, it is gradual and out of sight, “a violence of delayed destruction that is dispersed across time and space, an attritional violence that is typically not viewed as violence at all” (Nixon 2011, 2). And, although labelled as a ‘disaster’ (гамшиг) and ‘emergency’ (онцгой байдал), air pollution does not embody our visions of calamity—there are no images of explosions, instant death and destruction to evoke visceral reactions and feed our need for spectacle. Thus, it is precisely its character as ‘slow’—as a creeping cloud that slowly penetrates the body—that allows us to ignore it, but makes it that much more dangerous.
Although a human-made phenomenon, the slow nature of air pollution also makes it untenable for 4-year-term Mongolian political cycles. Due to the complexity of social change and resources needed to tackle the problem, the issue seems almost too big and too slow for any ruling political party to handle. Long-term effects of policy take a generation to take hold, long after the end of a politician’s tenure. And, as is often the case for man-made environmental phenomena (Nixon 2011), the ‘slow violence’ of air pollution “affects the poor above all else: Their unseen poverty is compounded by the invisibility of the slow violence that permeates so many of their lives” (4). Those with the luxury of choice through financial means can move further and further south, away from the plumes of smog, or even choose to spend their winters in another country. Yet, it is the ger district residents—those with the least means to change the situation and the most to gain from it—that remain in the city to breathe in the smog.
A Failure of Democracy
As previously mentioned, Ulaanbaatarites largely feel powerless to change the situation, and thus, the topic has lost its urgency (халуун сэдэв биш болсон мэт)[2]. Although mostly ger district residents breathe the worst of the air, a cloud is not containable, and inner city residents also increasingly feel the burden on their lungs. Yet, despite the unavoidable awareness of the smog (because it was everywhere), very little action was taken on part of inner city residents as well. In my experience, the individuals mostly wearing masks in the city were foreigners and foreign-educated Mongolians (e.g. NGO workers). People just mostly stayed indoors when it was bad (although they still breathe the air), and political outrage was all but absent.
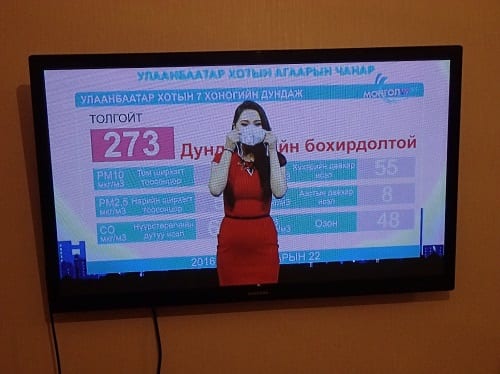
Inner city residents have become accustomed to reminders like this on the popular morning talk show Өнөө Өглөө (‘This Morning’). Yet, despite the awareness of air pollution, most residents are uninterested in wearing and/or unaware of how to acquire masks.
I asked Gansukh why he didn’t protest even though he was clearly very distressed by the smog. He told me the story about how his ger district was underserved and only had two kindergartens—which meant that wives frequently stayed home taking care of kids, while husbands were out chasing work opportunities. In his opinion, his region was purposefully neglected, because it kept people too busy (when they came home, they immediately had to get coal for the next day) to express grievances and left them without the time flexibility to change their situation. He expressed an interest in protest, but quoted a law that makes slander against politicians illegal.[3] They want us to be quiet (‘чимээгүй’), he said, they are just playing a game (‘тоглоом’) with us by pretending to fix things, while doing nothing in the interest of saving money and political face.
Whether or not Gansukh’s fears are true, they reflect widespread political sentiment and deep distrust towards the current state of political affairs. In political psychology, the term ‘relative deprivation’ describes when people compare the current state of their lives against a standard, like a human rights ideal or an understanding of how democracy should work (van Stekelenburg and Klandermans 2010). Protest is frequently motivated by the discrepancy between ideal and reality—when people feel that their current lives, environment and political situation fall short of the standard. Democracy itself is still relatively new to Mongolia (many people still feel like Mongolia is in a state of ‘transition’ [шилжилт]) and poorly understood (it is frequently assumed as ‘I have the freedom to do whatever I want’ especially based on money). Mongolian citizens, especially the poor, frequently do not possess a feeling of entitlement to a human rights standard—in this case, a life without poisonous air pollution.
In accordance with this conception of democracy, many Mongolians don’t feel like the current political situation answers to them. The term ‘political efficacy’ refers to a person’s expectation that they can alter a situation through protest. But simply, as Gansukh’s fears attest, many locals believe that politicians don’t act in their constituents’ interests, or that the system is open to being influenced by their needs. As both Gansukh and Odnoo echoed, politicians have been talking and talking about this subject for years (байнга ярьдаг), but haven’t done anything concrete (Яриж л байгаа болохоос биш хийж байгаа зүйл байхгүй). In fact, the only signs of awareness and change that I have seen these last months have been a proliferation of talk shows on the subject and the construction of billboards with the daily pollution numbers around the city. But, as Odnoo mused, “I already know it’s bad”, and thus felt that these boards weren’t telling her anything of substance. Consequently, there is no trust in government (итгэх итгэлгүй) to take tangible action and do what is beneficial for the long term prosperity of citizens. The ‘slow violence’ of air pollution is thus compounded by the slow reaction of politicians and government to act in a time frame beyond a four-year-political term.

Signs established by the now-defunct, government-funded Clean Air Fund give real-time updates on the quality of air in their respective areas according to the local Air Quality Index. Seen here in ‘Baruun Dorvon Zam’ and the 13th District indicating that the areas are enjoying a ‘low pollution’ day.
Conflicts of ‘Freedom’ and Future
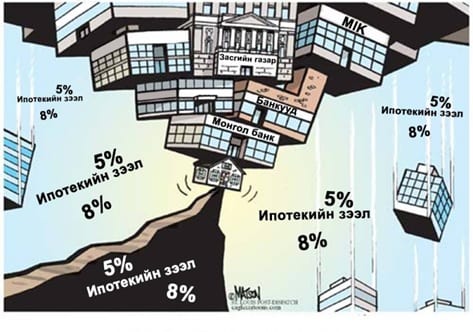
As elaborated in a recent post by Bumochir, actions that politicians have taken in the last years have been the implementation of a state-subsidized mortgage loan program, as well as the pursuit of ‘ger district redevelopment plans’ (гэр хороолол дахин төлөвлөлт). One justification for the hotly debated ‘ипотекийн зээл’—after its legality was contested in front of the Constitutional Court in December—was that it would also contribute to the reduction of air pollution. According to the logic in this argument, the loan program helps ger district families help themselves, by giving them the chance to afford previously unaffordable flats in the inner city. Similarly, in redevelopment plans, the state employs companies to rebuild a ger district into apartment complexes, redistributing the displaced families into flats. Thus, instead of overhauling infrastructure in the ger districts, families could just move into a flat with water, heating, etc., thus removing the need to burn coal.
This argumentation rests on the assumption that people in the ger districts want to live in flats. However, in my experience, ger district residents’ motivations are much more variegated. For example, in the ger district a family has much more space than they would have in a flat—as mentioned earlier, a 30,000,000 MNT (15,000 USD) land plot can easily accommodate multiple families, who can build houses according to their needs. In contrast, that amount of money wouldn’t cover the down payment in a size-comparable flat. In the ger districts, residents can hypothetically have dogs, build basketball courts, grow vegetables, cycle around and/or have a workstation. As one informant mentioned, he likes living in the ger district because of the ‘freedoms’—he is i.e. ‘free to scream’ if he wants to (чөлөөтэй орилж чадна). Here, his property is his ‘own’ (өөрийн гэсэн өмч), and wasn’t created, nor is controlled by someone else. He would only accept a ‘redevelopment plan’, he said, if they would move him to a similar plot somewhere else, so he could continue his lifestyle. In essence, many ger district families want to live in suburbia—want a plot of land and a house they can self-fashion according to their needs.
A video funded by the Japanese International Cooperation Agency (JICA) shows various versions of government-envisioned ger district redevelopment. Two of three include moving residents into flats of equal monetary value, which also frequently means a reduction in space.
This topic of immediate control over one’s environment is important for many ger district residents. For example, Ganaa, a 25-year-old pregnant teacher, lives in the ger districts with her husband. Like many others in her district of Hailast, she feels that the smoke has been almost unbearable these last months. But when I asked if she would consider moving into a flat, she emphatically said ‘never!’ To her, a flat represented an accumulated debt—like many others, her small family lives off her single income and can’t afford further debt accumulation. Asking people to move into flats can thus be perceived as asking those in debt to go even further in debt. Furthermore, unlike with a ger district plot, Ganaa doesn’t feel like a flat offers her control over her livelihood—to her, a ger is robust and allows her family to move or grow at will; whereas a flat is static and unchangeable. Instead of a living in a flat, Ganaa, like many others I talked to, ultimately plans to move to a countryside location close to the city (i.e. Baganuur). Thus, these plans labour under a clash of values and definitions of freedom; distrust towards government; and fears that relocation would mean that families are losing control over their own livelihoods.[4]
On the website www.agaar.mn, started by the government-funded Clean Air Fund, citizens can see real-time data on pollution levels around the city. Yet, although the trackers still work, other aspects of the site haven’t been updated since 2015—when the program was shut down due to ‘decrease[d] government spending’ (http://ubpost.mongolnews.mn/?p=16979). More than different numbers and colours, the variability of pollution levels reflect a map of disenfranchisement and social disparity across the landscape of the city. Instead of flats, ger district residents would prefer reduction in electricity costs and better infrastructure; government plans to decentralise power and wealth to the countryside in order to curb migration; and financial support for solar panels and alternative energy. Thus, although ger district resident actions might seem illogical to some, they are enjoying the freedoms that they have within limited choices. Ultimately, the problem of ‘slow violence’ can only be addressed through ‘slow thinking’—a switch from short-term, immediate-gratification rationale to long-term investment decisions that ultimately benefit the good (and the lung health) of all.
Acknowledgements: I want to thank my team for inspiration on this topic, as well as Ganza, Nomin, Anji and Froit for putting up with my questions.
[1] According to a recent interview with the country director for the World Health Organisation, there were 435 registered cases of miscarriage due to no growth in 2015 at the National Center for Maternal and Child Health. See http://agshin.mn/index.php?newsid=1725
[2] As per a statement by the host on a popular political debate show Нүүдэл Шийдэл (translated roughly as ‘Decisive Action’): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=atd2FWn-SkQ
[3] Probably in reference to a provision in the recently newly-passed Criminal Law (December 2015) that makes distributing false information during an election punishable.
[4] As a result of these clashes, the Gandan district authorities recently announced that they were discontinuing a ger district development plan in the area due to chaos and lack of consensus. See, i.e., the news report ‘Гэр хорооллын дахин төлөвлөлтийн ажилд иргэд өөрсдөө ч саад болж байна’ (‘Citizens involved in redevelopment programs are blocking their own progress’) at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qc_9RGqkces
References
Nixon, R. 2011. Slow Violence and the Environmentalism of the Poor. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
van Stekelenburg, J. and Klandermans, B. 2010. The social psychology of protest. Sociopedia.isa (available on-line: http://www.surrey.ac.uk/politics/research/researchareasofstaff/isppsummeracademy/instructors/Social%20Psychology%20of%20Protest,%20Van%20Stekelenburg%20%26%20Klandermans.pdf)
 Close
Close