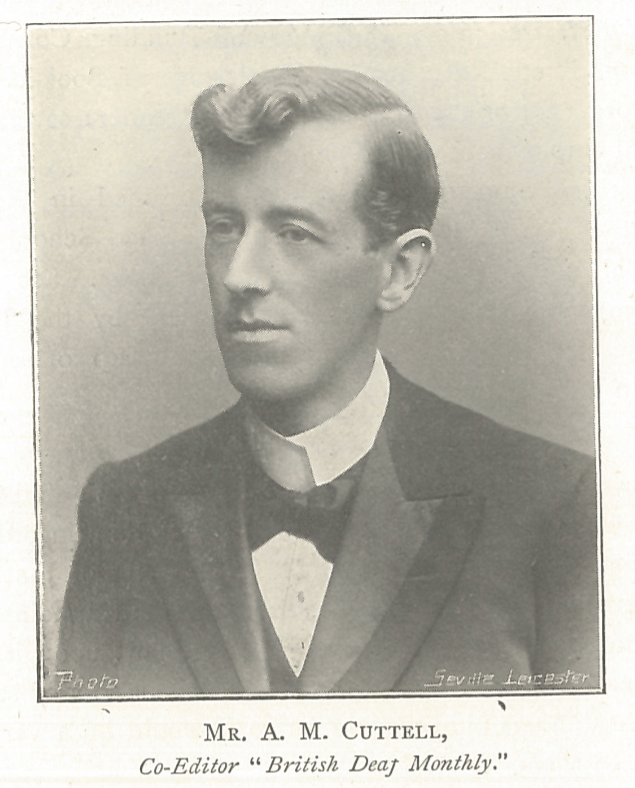
 George Annand Mackenzie, (1868-1951) was the first born deaf man to obtain a degree from a British university (B.A. in Theology, 1910, Master of Arts, Cambridge, 1911).*
George Annand Mackenzie, (1868-1951) was the first born deaf man to obtain a degree from a British university (B.A. in Theology, 1910, Master of Arts, Cambridge, 1911).*
Born to Scottish parents, his father was a chief reporter for the Liverpool Mercury (census, 1881). He was not the first in his family who was deaf. His elder brother, James Wilson Mackenzie (1865-95), was a talented artist, but he died young, and his obituary appeared in his father’s paper. I wonder if their father wrote it –
THE LATE MR WILSON MACKENZIE.—Poignant regret is kindled in the hearts of his old masters, his old fellow-students, his nearer circle of friends, and the wider range which embraces those whose admiring appreciation is confined to true art, by the announcement of the death of Mr. J. Wilson Mackenzie, eldest eon of Mr. J. B. Mackenzie, of Liverpool, the sad event having occurred at West Kirby on Tuesday night. Early in his youth Wilson Mackenzie developed a remarkable aptitude in drawing and a fine sense of colour. He was placed under Mr. John Finnie, the principal of the School of Art, in Mount-street, and after a prolonged course of tuition in that nursery of painters, passed over to Paris, where he spent some time in the famous studio of Bougereau. While on the very threshold of his career, and later, he was an honoured exhibitor at the Royal Academy, and on many occasions works from his easel were hung in the Autumn Exhibitions in the Walker Gallery. In portraiture he ever minced the highest qualities of perception of charterer, and notable examples of his rare gifts in this direction are to be found inks presentments of the late Dr. E. M. Sheldon, Dr. J. Kona Smith, the late Police Magistrate of Birkenhead (Mr. J. Preston), and the into Dr. Costine. Some few years back signs of failure of the young painter’s health began to assert themselves, and in search of restoration he repaired to Davos Plata. For a time the change gave rise to hopes of recovery, but these, alas, faded away, and he returned home a. few months ago to die amongst those he loved so well. Wilson Mackenzie—it is agreeably easy to recall his eyes, quick with the brightness of genius, his graceful features, and his buoyant demeanour—was of a singularly sweet disposition, and all who know him, and knowing him therefore esteemed him, share with his parents. his sister, and his brothers the grief with which the calamity of his untimely demise has overshadowed their household. The funeral is to take place at. West Kirby Parish Church, at three o’clock to-morrow (Friday) afternoon. (Liverpool mercury, 1895, 1oth October)
In fact, the 1881 census says that George was ‘semi-deaf from birth,’ suggesting that at least when younger he had some hearing. His mother sent him to live in Perthshire with an uncle who farmed , in the hope that the climate would help his hearing, but he seems to have run wild and was so shy on his return that he hid when he was re-introduced to his older brother (Silent World 1951, p.266). We also read that he – and presumably his brothers – was taught initially by his mother “in finger spelling and signing – arts in which she was adept” which makes one wonder whether she learnt to help them or had learnt from some deaf relative. Robert Armour (1837-1913), Missioner for the Deaf in Liverpool (born in Kilmarnock and deafened at 18 months by “some malady of the brain”) gave him some instruction in English composition, and he and his brothers walked five miles to the nearest church where services for the Deaf were held, so they met other members of the local Deaf community, like George Healey.
At thirteen after irregular attendances at a junior school, he went to a large hearing school, where the classes were too big and the teachers overworked. Being the only deaf pupil there he received scant attention. His school-mates with the thoughtless cruelty of the young made fun of him, standing around the door when class was dismissed and waving their hands and fingers in mimicry of his only means of expression. He took all this, he says, in good part, refusing to be drawn into any manifestation of anger or weakness and his good natured smiles soon made the game lose its savour and turned most of his tormentors into staunch and understanding friends. (Silent World p.266-7)
He was pretty much left to work out lessons for himself, gazing at pages of fractions and decimals until he understood, and he was successful enough to win school prizes (ibid). His mother encouraged him to use his voice, but in The Teacher of the Deaf (1910, p.150) we read “He owes his mental development to the manual method.”
Leaving school, he became an artist like his brothers, winning prizes, and painting portraits of Sir Edward R. Russell , Dr. Robert Jones, and the Rev. T.W.M. Laud, among others. He worked as an art master at a Liverpool school, and a potterty designer in Derby, before becoming a missioner to the deaf in 1901. He then worked in Ely, Oxford and Cambridgeshire, before going to Cardiff from 1921 until his retirement in 1931.
He had tried to enter Liverpool University, with no success, and was also declined at Oxford when he was missioner there. In 1907 the Cambridge University academics were however more enlightened than their Oxford colleagues, and he was accepted as a student. He was excused lectures and spent the days reading for six to eight hours. He graduated in 1910, causing a minor splash in newspapers of the time.
George married a Deaf lady from Cambridgeshire, Emily Lucy Kett (a good Norfolk name!) (1873-1954), and they had the one child, Alan. He became involved in the deaf community, not really surprisingly, and went into the church. The Rev. Alan F. Mackenzie (1911-1997) worked for the R.A.D.D. and was at one time on the council of the N.I.D.
The younger brother, Charles Douglas Mackenzie (1875-1953), was also Deaf. He too became an artist, and seems to have made a living out of it. He remained living with their mother after his father died. Unfortunately I have not had time to research him properly.
 *There is always the slim possibility that someone sneaked through before this, unrecorded.
*There is always the slim possibility that someone sneaked through before this, unrecorded.
1871 Census – Class: RG10; Piece: 3849; Folio: 124; Page: 54; GSU roll: 841928
1881 Census – Class: RG13; Piece: 3419; Folio: 6; Page: 3
British Deaf Times, 1910, 7, 169-170
Grand Old Gentleman, Silent World vol.5 (9) 1951 p.266-8
The Messenger, 1910 vol.10 (6) p.80-82
Obituary. Teacher of the Deaf, 1951, 49, 154
ROE, W.R. Peeps into the deaf world. Bemrose, 1917. pp. 186-92.
Teacher of the Deaf, 1910, 8, 149-151. (photo)

 Mary Ann Frances Burnell was born in Cosgrove, Northamptonshire, in 1857, daughter of a labourer, William Burnell (aslo Burnal) and his wife, Elizabeth. She was not described as deaf in the 1861 census when she was three, but a later census says she was ‘deaf from birth’ (1891). She had at least one hearing brother and sister surviving, but many more that died very young.
Mary Ann Frances Burnell was born in Cosgrove, Northamptonshire, in 1857, daughter of a labourer, William Burnell (aslo Burnal) and his wife, Elizabeth. She was not described as deaf in the 1861 census when she was three, but a later census says she was ‘deaf from birth’ (1891). She had at least one hearing brother and sister surviving, but many more that died very young.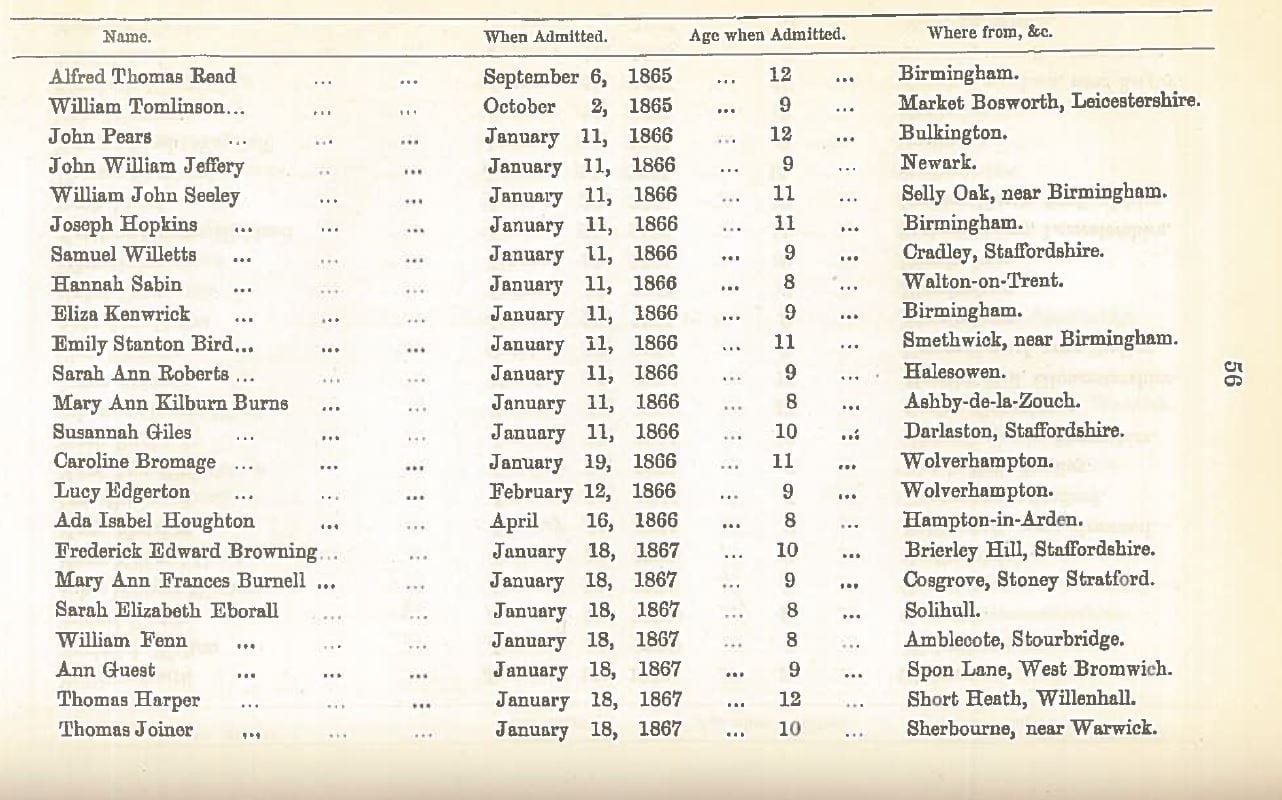
 1861 Census – Class: RG 9; Piece: 927; Folio: 29; Page: 16; GSU roll: 542722
1861 Census – Class: RG 9; Piece: 927; Folio: 29; Page: 16; GSU roll: 542722 Close
Close


























