“His appearance is mild, but rather sullen” – a Manslaughter charge against a Deaf man in Manchester, 1853
By H Dominic W Stiles, on 25 October 2019
I came across the following story from the Manchester Courier and Lancashire General Advertiser for Saturday the 10th of December, 1853:
Charge of Manslaughter against a Deaf and Dumb Boy.
John Flannagan, a deaf and dumb youth, was charged with killing a boy named John Stanley, on the Garratt-road, near Manchester, on the 17th September, by throwing him into the canal. The prisoner being deaf and dumb, the proceedings attendant on the investigation created considerable interest. Mr. Andrew Patterson, teacher in the Deaf and Dumb Institution, at Manchester, was sworn to act as interpreter. -It appeared the prisoner had been an inmate of this institution for three years, and was considered a lad of considerable aptitude and sharpness. Mr. Monk prosecuted, and Mr. Wheeler defended. After some discussion between the legal gentlemen, it was admitted that the evidence was insufficient to establish so serious a charge manslaughter. On investigation it appeared that the prisoner and another boy were proceeding along the road when they were joined by the deceased, who soon after attempted to take a stick from one of the boys, and the prisoner seized hold of him. A struggle ensued, and deceased was tumbled into the canal.
This is very interesting, but John Flannagan proved tricky to pin down. The article says he was a pupil at the Manchester School for three years, so he ought to be on the list of pupils for 1851 and 1852, years we have school reports for, and one would expect he would also be on the list of pupils for the 1851 census, but I could find no mention of him in either place. We have Andrew Patterson sworn in to interpret in court, although it is not clear that his services were required. Furthermore, we see a Deaf person coming out the right side of justice. A sad and unfortunate story, with an appropriate ending, or so I thought.
However, the story is more complicated. Newspapers today frequently get facts wrong and misspell names, and that was equally true in the past. When no amount of searching gave me a hint of John Finnigan, I looked again at that report. I realized it said he ‘had been’ an inmate of the institution, so he was a bit older. I looked at the earliest annual report we have for the school, 1850, and there is a John Finnigan, aged 15 in March 1850, from Manchester, “father a nailer, 2 deaf and dumb” admitted to the school July 28th, 1845. 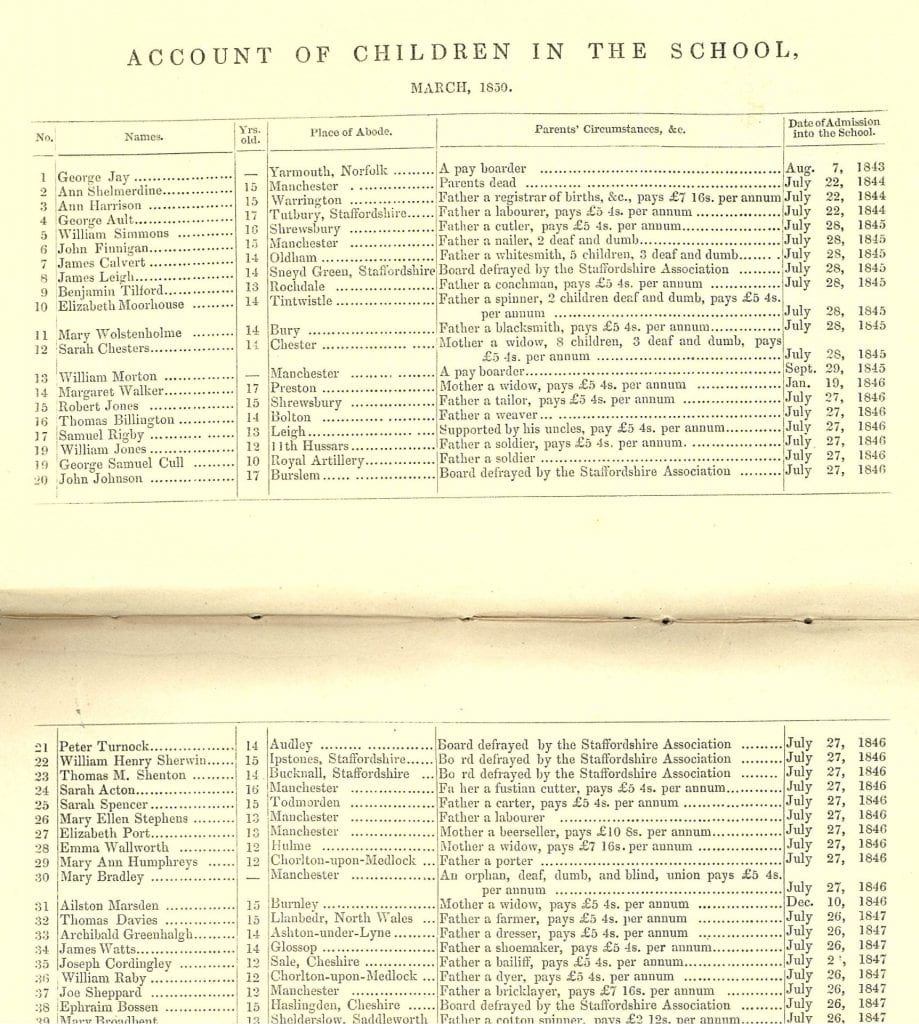 Now we were getting somewhere, and a new search of the newspaper archive found an earlier version of the story, from September, just after the incident, which gives it a completely different slant. This came from the London Daily News for Thursday the 22nd of September, 1853:
Now we were getting somewhere, and a new search of the newspaper archive found an earlier version of the story, from September, just after the incident, which gives it a completely different slant. This came from the London Daily News for Thursday the 22nd of September, 1853:
THE MURDER AT MANCHESTER.
John Finnigan, the deaf and dumb boy, charged with the murder of James Shanley, a child six years old, by throwing him into the Rochdale Canal, at Manchester, on Saturday, was again brought up for examination, yesterday, before the magistrates at the Manchester City Police Court.Betsey Shanley, the mother of the deceased, said her son left home between 5 and 6 o’clock on Saturday evening, and she never saw him alive afterwards.
Thomas Shanley, the father of deceased, said, I live at 13, Taylor’s-court, Oxford-street. I called at all the police-stations on Saturday night, and did not return home till past two o’clock on Sunday morning, and on Sunday I made time same round again, also calling at the workhouses, without obtaining any information whatever of my son. I and another man found him in the canal on Sunday after- noon, between 2 and 3 o’clock.
Angus Thorley, a little boy, ten years of age, who in giving his evidence, displayed considerable dullness of apprehension, said, I was going up Garratt-road for a walk on Sunday, with another boy, when two boys came behind us. One of them was going to throw me into the canal, and the other got hold of the boy who was with me, by the clothes, and threw him into the water. I know it was Sunday.
Alderman Walker- What day did you say it was when you were here before ?
Witness – I said it was Sunday. I don’t know what time it was. We were going over the bridge. I go some- times to school on Sunday, but I could not go that day. There were no workmen or carts about. I don’t know when I told my mother about it. I had never before seen the boy who threw the deceased into the canal, but I know the prisoner is the same. I am sure he did it on purpose, and then he ran away.
Mr. Superintendent Taylor, of the Manchester police, said this boy (the last witness) came to the Police-office shortly after 10 on Monday morning with his mother and the deceased’s father, and stated that on Saturday [not Sunday] evening he was taking a walk up Garratt-road with another boy, when the prisoner came up and threw his companion into the water.
Mrs. Thorley, the mother of the witness Angus Thorley, said – My son came home on Saturday night about seven o’clock, looking very downcast, and laid his head against the wall. He has often been stoned and ill-used by other boys in the street, and I thought they had been molesting him as usual. On Sunday night, after the body had been found, I was putting him to bed, when he laid his head on his breast, and said ” Mamma, I have seen the little boy that was drowned;” and afterwards started up and exclaimed “I saw him throw him in though.”
There being no further evidence, the prisoner was remanded till Friday.
Mr. Pattison [sic], master of the Deaf and Dumb School at Old Trafford, interpreted the evidence to the prisoner, who seemed, by signs and gestures, indignantly to deny every- thing that appeared to criminate him. He is said to be a very intelligent boy, and can write very well. He is apprenticed to a joiner, and his father is a nail maker, residing in Chorlton-upon-Medlock. The prisoner was educated in the Deaf and Dumb School, where he had the character of a very headstrong and self-willed boy, but never manifested a disposition from which it could be inferred that he was likely to commit a serious crime like this. His appearance is mild, but rather sullen.
Further reports emerge, all with some slight variations of names and spelling, due to the mis-hearing of names & having to guess at spellings for names heard in court. The Sun (London), for Thursday the 22nd of September, 1853, repeats that report, verbatim. The Stamford Mercury for Friday the 16th of December, 1853, has the victim as ‘James Shandley’. One of the papers tells us the victim was six years and eight months old.*
Another version in the Manchester Times for Saturday the 24th of September, 1853, gives the fullest account of the original hearing [I have added some paragraphs not in the newspaper, to make it easier to read]:
WILFUL DROWNING OF A BOY IN THE CANAL
On Wednesday, at the City Police Court, John Finnigan, a deaf and dumb lad, aged eighteen, was again brought before the magistrates upon the charge reported in our last paper, of having caused the death of James Shanley, a child of six or seven years old, by throwing him into the canal adjoining Messrs. Bellhouse’s timber yard, Garratt Road. The prisoner’s parents live at 31, Leigh-street, Chorlton on Medlock, and he himself is apprenticed to Mr. M’Lean, builder, on the Stretford New Road; he has been five years in the Deaf and Dumb Institution, at Old Trafford, and, in despite of the deprivation of his senses, he is considered intelligent, and has been usually well conducted; he can read and write well. The child whose death was the subject of inquiry belonged to a poor man’s family, at 18, Taylor’s Court, Oxford Road. His mother states that he went out to play between five and six o’clock on Saturday evening last, and never returned. His father, Thomas Shanley, went in search of him on Saturday evening, and called at all the police stations in the town, but could hear no tidings of the child that night. On Sunday morning, he went out again early, and continued his search; went to the workhouses and other places, but could get no intelligence of the lost boy. It was between two and three o’clock on Sunday afternoon, when the dead child was found in the canal by his father, assisted by a young man of the neighbourhood. On Monday morning, the father of the dead child, accompanied by a little boy named Angus Thorley, with his mother, came to Mr. Taylor, the ‘superintendent of police at the Chorlton Town Hall, to make known the statement of the boy Angus Thorley. This witness, who is ten years old, told Mr. Taylor then, that, on Saturday evening, he was with the other child, James Shanley, whose name he did not know ; and that, in their play, they walked along the canal by the Garratt Road, and he there saw the prisoner, with another big boy ; and that, after a short time, although nothing had been done or said between them, the prisoner caught up the little fellow Shanley, who was with witness, taking hold of his clothes behind, and threw him into the water, and then ran away—that he (the witness) ran after the prisoner, but could not overtake him, and that some one told him it was “the dummy boy”. The mother of Angus Thorley described the manner in which her son came to tell her this story of what he had seen. She said: I was very strict with him, and frequently forbid him to go near the water (which might amount for his not mentioning the matter to his mother at first). On Saturday afternoon, be came home to be washed, about five o’clock, and when he came home he was not like as at other times, but he laid his head against the wall, and was very quiet. I noticed him then, but I thought it was because some of the Irish boys, who have a great antipathy to him, and have stoned him several times, had been at him as usual. I washed him myself, as I always do, and put him to bed, and nothing more was said by him that night, only that several times after be asked me for drink, and his aunt also gave him water to drink. On Sunday night, he was going to bed at the usual time, and I was up with him myself, and put him to bed ; but when he was undressed, he sat on the ground, and held his head on has breast; end at last he said to me, “Mamma, I’ve seen that little boy that was drowned,” and I said, “What little boy ?” for I had not heard then of the other child being lost; and he said, “The little boy that was thrown into the canal !” I said, “What do you mean, child ?” Then he looked up and said, “I saw him throw him in,— he’s black, mamma, and he had salt on his stomach.” This means the corpse of the child, which, when it was taken out of the canal, was discoloured, as commonly happens with dead bodies, so probably, the boy, Angus Thorley, had been lingering about the place on Sunday afternoon when the dead child was taken out, and had seen salt rubbed into the abdomen, in the hope of restoring life. The boy having told his mother the story of what he had witnessed, she took him to the father of the dead child Shanley, and he brought them to the police superintendent. The boy was again examined by the magistrates on Wednesday ; Mr. Gray, of the office of Mr. W. P. Roberts, attending as attorney for the prisoner, and Mr. Patteson [sic], of the Deaf and Dumb Institution, to interpret the evidence to the prisoner.—The young witness was evidently confused, but his manner was very childlike and simple; he said now, differently from what he had said on Monday, that it was Sunday afternoon, instead of Saturday. when he saw the prisoner throw the child who was playing with him into the water; the place was “just as they were going over the bridge beside where they wind the planks up.” He seemed quite sure, on looking at the prisoner, that he was the same person who threw the boy in,—and that he threw him in on purpose, not accidentally; he (the prisoner ), with another boy, were coming behind witness and the deceased, over the bridge, when the prisoner caught hold of the loose skirts of his clothes behind, lifted him, and threw him into the canal, and then “chased off”. No other person was near at the time. The witness repeated, that this happened on Sunday ; but he did not seem to know much of the days of the week; he went to a Sunday-School “sometimes,” but had not been to school that day. At present, no information could be obtained as to the other lad, who was stated to have been with the prisoner when this was done; and the prisoner had nothing to say for himself, or was advised by his attorney to say nothing. He was, therefore, remanded to Friday for further inquiry.
—He was again brought up yesterday, and discharged from the custody of the court.
–The coroner for the city, Mr. Herford, held an inquest on Wednesday afternoon, at the Royal Infirmary; when the prisoner, with his attorney, were present; and the boy, Angus Thorley, then repeated his original statement, in the following words:—On Saturday afternoon, me and the boy that is dead were going up the hill out of Garratt Road, and going across the bridge over the canal at the timber-yard; and that boy (the prisoner) and another boy came behind us. I said to the boy that was with me,”Cut away;” and he (the deceased probably) tried to take the stick from me; then, the master was coming, and the other boy (who was with the prisoner) ran away. The dummy boy then laid hold of the boy who was playing with me, taking him by the clothes, with one hand his neck and the other his back part, and threw him in; his feet went first into the water. The dummy boy then ran away and turned up an entry, but he did not get into Garratt Road. I did not see him again; I had never seen the “dummy” boy before. In reply to questions from Mr. Gray, the boy said: I know I told the magistrates that that this was on Sunday, but it really was on Saturday, it was about five o’clock, and as light as it is now. I had no quarrel about the stick with the boy that is dead; but he wanted it, and took hold of it.
—The superintendent of police stated that the witness had picked out Finnigan, the deaf and dumb lad, from amongst five others, and identified him as the one who threw the little fellow into the water. He had, also, shown them the place on the canal bank, which was about thirty yards distant from the place where the corpse was found; but if the locks were open there would be current strong enough to carry the body that distance, there is a coping stone three-quarters of a yard above the water.
—Mr. A. Paterson, surgeon, had examined the body, but found no marks of violence ; drowning was the cause of death.
—The inquest terminated by the jury finding a verdict of “Manslaughter” against John Finnigan, who has been, accordingly, committed for trial.
Further reported in the Liverpool Mercury for Tuesday the 27th of September, 1853, the writer says “The evidence was very meagre and unsatisfactory. […] The prisoner had a man with him, who also attempted to throw Thorley in. Prisoner and the man ran away, and Thorley says he ran after the prisoner, and saw no more of Shanley.”
Here we have Thorley saying someone else was there who attempted to throw Thorley in to the canal.
In the Kentish Gazette for Tuesday the 27th of September, 1853, Thorley’s mother said that he
has often been stoned and ill-used by other boys in the street, and thought they had been molesting him as usual. […] Mr. Pattison, master of the Deaf and Dumb School at Old Trafford, interpreted the evidence to the prisoner, who seemed, signs and gestures, indignantly deny everything that appeared to criminate him. He is said to be a very intelligent boy, and can write very well. He is apprenticed to a joiner, and his father is nail maker, residing in Chorlton upon-Medlock. The prisoner was educated in the Deaf and Dumb School, where he had the character of very headstrong and self-willed boy, but never manifested a disposition from which could be inferred that he was likely to commit serious crime like this.
It seems to me that there is far more going on here than has emerged in any of the court sessions. All I have is various suspicions and more questions. Clearly Thorley was the subject of bullying ‘by the Irish boys’ which perhaps might include Finnigan, but whatever the story was with the stick, we can only guess. Did Thorley invent the story to cover an argument he had with Shanley? Who was the fourth person, the young man with Finnigan, and what was that about “the master was coming” – who was the master? Why did Thorley run after Finnigan and not cry out for help? Why do we hear nothing from Finnigan, if he was innocent? Thorley was supposed to be 10, however the only person I can find on the census who seems to match, is an Angus Thorley who became a porter, dying aged 38 in 1885. There are not many Angus Thorleys, so I am confident that this is him. That suggests that he was only six years old at the time of the death of James Shanley, rather than ten.
Was the victim James or John, Shanley or Shandley or Stanley?! You see the problem with using newspapers as historical sources. The Morning Post for Thursday, the 8th of December, 1853, has a name that is impossible to ready but must be James —ley. I have not definitively found his death record, or his family.
There is more to be found on Finnigan. In 1859, at Manchester Cathedral, he married a Deaf girl, Eliza Barlow (1837-78). Eliza was born in Staffordshire, at Newcastle under Lyme, and was described as Deaf and Dumb on the 1851 census. She was at the Manchester Deaf school as well. John Finnigan was born in Manchester, according to the 1861 census, but in Ireland, according to the 1871 census, when he was living in Hulme as a Pattern Maker. The 1881 census has his age as 30, with him born at Salford, Eliza being dead by then. His marriage record tells us that he was a son of Thomas Finnigan, nailer, so we can be sure that he is the right Finnigan. I cannot find him in later census returns but an ancestry family tree has him dying in 1924. John’s brothers were also pupils.
In the school register, on a page kindly sent to me by our great Deaf History sleuth Norma McGilp, it tells us John was born on the 25th of March, 1835. It adds in the comments field, information from the Rev.Downing who ran the Manchester Adult Society, presumably added in 1878 –
The eldest of the four Deaf and Dumb in the family, and probably the best of them, but he married a Deaf and Dumb woman of intemperate habits, by which she hastened her death, and whom I buried last week. Their eldest daughter is the mother of an illegitimate child.
I do not know Manchester so pinning down the locations with name changes of streets is not easy, but this is where the Bellhouse building was here but was I assume not where the timber yard was, which must nonetheless be in central Manchester. Please comment if you know where Garratt Rd. was, or can pinpoint the spot where the tragedy occurred.
In addition to the papers quoted above –
*Manchester Courier and Lancashire General Advertiser – Saturday 24 September 1853
Morning Post – Thursday 08 December 1853
Manchester, England, Marriages and Banns, 1754-1930 (Cathedral)
Eliza Barlow –
1851 Census – Class: RG10; Piece: 4002; Folio: 19; Page: 31; GSU roll: 846101
John & Eliza Finnigan –
1861 Census – Class: RG 9; Piece: 2921; Folio: 31; Page: 6; GSU roll: 543050
1871 Census – Class: RG10; Piece: 4002; Folio: 19; Page: 31; GSU roll: 846101
John Finnigan –
1881 Census – Class: RG11; Piece: 3962; Folio: 7; Page: 7; GSU roll: 1341946
Angus Thorley –
1881 Census – Class: RG11; Piece: 3887; Folio: 47; Page: 41; GSU roll: 1341928
 Close
Close
















