Young people’s engagement with extra-curricular activities following the pandemic
By Blog Editor, on 19 June 2023
COSMO researcher, Alice De Gennaro, documents young people’s extra-curricular engagement in the aftermath of the pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused significant disruption to all of our lives. The disruption to young people’s lives was well-documented across a wide range of areas including education (during and after lockdowns), future plans, wellbeing, and health. One area that has received less attention is young people’s continuing engagement with extra-curricular activities. But this is an important topic given the potential benefits of taking part in such activities. In the second analysis of this series, we show that there is a positive relationship between extra-curricular engagement and measures of wellbeing and students’ levels of exercise.
In this blog post analysis, we explore changes in such activities from before the pandemic to during the period of ongoing disruption in the academic year 2020-21. We find significant reductions in extra-curricular activities both in and out of school and a reduction in intensity where activities did continue. These changes were larger for some groups than others, especially by school type and gender.
What did we ask students?
Students were asked if they engaged in five kinds of extra-curricular activities both before the pandemic started when students were in Year 10 and when schools reopened when students were in Year 11. The five types of activities were: sport, other club, religious activity not including regular worship, community or voluntary work, and overnight organised activities. Students were asked if they took part in each of these activities. Among those who did take part, they were further asked if this activity was organised by their school or externally, or both. It is important to note that these questions mean our measures reflects how a student took-up an activity (if they did) rather than whether or not an activity is being offered (because we only know the type of provision conditional on them having taken part).
How did the take-up of extra-curricular activities change during the pandemic?
Unsurprisingly, there was a drop in the total take-up of extracurricular activities after the onset of the pandemic, compared to before it started. The proportion of activities being undertaken that were provided by schools were cut roughly in half for all activity types. Take up of externally provided activities dropped, too, but to a lesser extent.
Figure 1. Take-up and type of provision of extra-curricular activities in year 10 (pre-pandemic) and year 11 (schools open) (N=6,286)
The table below shows the proportion of students continuing with each extra-curricular activity in year 11 given that they took part in it in year 10, regardless of the type of provision. Sporting activities had the highest rate of continuation while overnight activities were much less likely to be resumed.
Table 1. Proportion of students continuing with extra-curricular activities in year 11

Students were also asked how often they did extra-curricular activities (excluding overnight stays) in both periods. Among those who reported any extra-curricular activity in year 10 (N=2,843), we found that 28% of students decreased their frequency of activity, 61% kept it the same and 12% took part in activities more frequently.
Looking into the differences in frequency of activity in both time periods, we find that young people were tending to take part in extra-curricular activities fewer times per week, with 3% of those who previously responded as participating with some frequency, saying they never did any activities in year 11. While 46% of students participated three or more times a week pre-pandemic, this dropped to 37% when schools re-opened.
Figure 2. Frequency of extra-curricular activities in year 10 and year 11 (N=2,796)
How did continuing engagement vary?
To get a more holistic understanding of changes in extra-curricular engagement, we constructed a measure of how many activities students continued with when schools reopened compared to before the pandemic. By definition, we could only construct this measure among those who did take part in at least one activity pre-pandemic. By looking at how this measure varies across some key socio-economic and demographic characteristics, we find some interesting patterns.
Girls stopped all activities in greater proportions than boys and were less likely to continue with both 1-2 and 3+ activities. In a follow up analysis, we discuss what these gender differences in engagement might mean for their health and wellbeing. Overall patterns of engagement across ethnic groups were not starkly different.
Figure 3. Continuing engagement by gender (N=6,286)
Figure 4. Continuing engagement by ethnicity (N=3,898)
Students from state schools were more than three times more likely to stop all activity and three times less likely to continue with three or more activities than their peers in independent schools. For every activity, the proportion of students doing activities organised by their school was highest among those at independent schools, most markedly for sport. Furthermore, pupils from independent schools overall took part in more activities in both school years. While we might expect that independent schools are able to organise more activities for their pupils, Table 2 illustrates a potential link between greater school provision and total extra-curricular engagement (including external). In other words, lower school provision (proxied by lower rates of extra-curricular take-up in schools) may not lead to pupils taking part in more activities outside of school — they seem to be complements rather than substitutes.
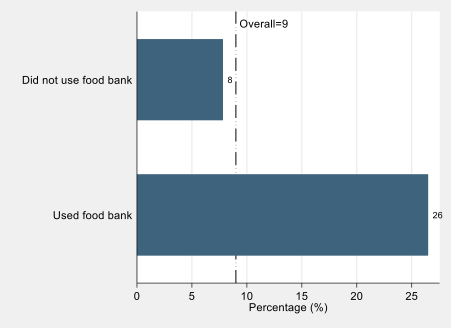
Young people living in more deprived neighbourhoods (as measured using IDACI, a widely used measure of income deprivation) stopped all extra-curricular activities in greater proportions than those in more affluent neighbourhoods, with an 18-percentage point difference between the least and most deprived quintile groups. This tracks across the other categories, too, as we see that higher deprivation is associated with proportionally fewer students continuing with one or more activities.
Figure 5. Continuing engagement by carer status, school type, IDACI (N=4,334)
Table 2. Total number of extracurricular activities by school type in Year 11(N=6,261)

Young carers were less likely to stop and more likely to continue with three or more activities than their peers without caring responsibilities. This might be surprising if young people with caring duties have less time to spend on extra-curricular activities compared to those without such responsibilities. Looking further into this by activity type, we found that carers had higher proportions of continuing with every activity compared to non-carers, especially community activities which might represent a certain civic mindedness. Interestingly, the proportion of students taking part in each activity pre-pandemic were similar across both groups. It is only once schools re-opened that differences emerge, and carers show higher rates of participation.
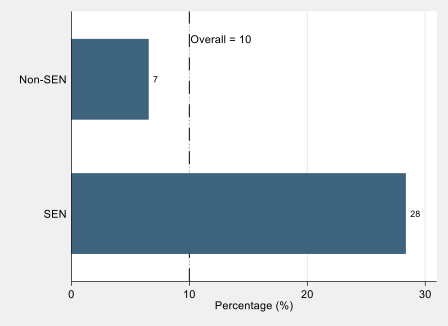
Continuation of extra-curricular activities was also strongly linked to parents’ socio-economic status. The children of parents without a degree were less likely to continue with any activities than those whose parents do have a degree. Young people with parents who have a degree were also more likely to continue with one or more activities compared to the other group.
The children of parents with lower occupational status jobs were much more likely not to continue with any activities, with a 15-percentage point difference between those from routine backgrounds and those from managerial and professional backgrounds. The proportion of those from intermediate backgrounds continuing with three or more activities was around half that of the other two groups.
A similar story appears by housing tenure and so it thus appears that children from more disadvantaged backgrounds were less likely to re-engage with extra-curricular activity once schools reopened, even among those who took part in such activities before the pandemic.
Figure 6. Continuing engagement by parent characteristics (N=2,405)
Conclusions
The take-up of extra-curricular activities done in or out of school and the frequency with which students did them, dropped once schools re-opened compared to their previous academic year before the pandemic started. It is important to note that disengagement from extra-curricular activities may have occurred had the pandemic not happened. The prospect of upcoming Year 11 exams and more generally being older are some reasons why this could be the case and this analysis does not allow us specifically to isolate the effects of the pandemic on extra-curricular engagement. Nevertheless, our findings highlight important patterns with potential implications for other aspects of students’ lives.
While it may have been expected that the overall take-up and frequency of extra-curricular activities was dampened once schools reopened, this was far from equally spread among students from different backgrounds. Concerningly, across various measures and correlates of socio-economic background (school type, IDACI, NS-SEC, parental education and housing tenure) we see a similar pattern of students from more disadvantaged backgrounds re-engaging with extra-curricular activities to a much lesser degree compared to their more advantaged peers, echoing findings from Social Mobility Commission before the pandemic. Furthermore, girls had lower levels of engagement with extra-curricular activities in the wake of the pandemic, and we discuss in the following analysis how this pattern might interact with health and wellbeing.
On a positive note, sporting activities saw the highest rate of continuation, which is promising for both physical and mental health, given links between exercise and wellbeing. There was also little difference in patterns of engagement by ethnic groups and, despite their additional responsibilities, carers had higher rates of extra-curricular engagement.
Extra-curricular engagement leads to a range of positive outcomes for young people, especially as UK employers increasingly demand soft skills, which may be developed via extra-curricular engagement. This engagement may thus be important for intergenerational social mobility. Young people from disadvantaged households already face several barriers to extra-curricular engagement and the pandemic seems to have exacerbated this.
But what might be some other potential implications of differences in continuing engagement in extra-curricular activities? Our follow-up analysis dives deeper into the relationship between extra-curricular engagement and quantity of exercise with student health and wellbeing, finding positive impacts on mental health and self-esteem.
This is the first piece in a two-part analysis.
 Close
Close