Student presentation – Alex Hawkins Hooker at ISMB
By sharon.betts, on 4 October 2023

 Close
Close

By sharon.betts, on 4 October 2023

By sharon.betts, on 29 September 2023
In the exciting realm of Model-based Reinforcement Learning (MBRL), researchers are constantly pushing the boundaries of what robots can learn to achieve when given access to an internal model of the environment. One key challenge in this field is ensuring that robots can perform tasks safely and reliably, especially in situations where they lack prior data or knowledge about the environment. That’s where the work of Sicelukwanda Zwane comes into play.
Background
In MBRL, robots use small sets of data to learn a dynamics model. This model is like a crystal ball that predicts how the system will respond to a given sequence of different actions. With MBRL, we can train policies from simulated trajectories sampled from the dynamics model instead of first generating them by executing each action on the actual system, a process that can take extremely long periods of time on a physical robot and possibly cause wear and tear.
One of the tools often used in MBRL is the Gaussian process (GP) dynamics model. GPs are fully-Bayesian models that not only model the system but also account for the uncertainty in state observations. Additionally, they are flexible and are able to learn without making strong assumptions about the underlying system dynamics [1].
The Challenge of Learning Safely
When we train robots to perform tasks, it’s not enough to just predict what will happen; we need to do it safely. As with most model classes in MBRL, GPs don’t naturally incorporate safety constraints. This means that they may produce unsafe or unfeasible trajectories. This is particularly true during early stages of learning, when the model hasn’t seen much data, it can produce unsafe and seemingly random trajectories.
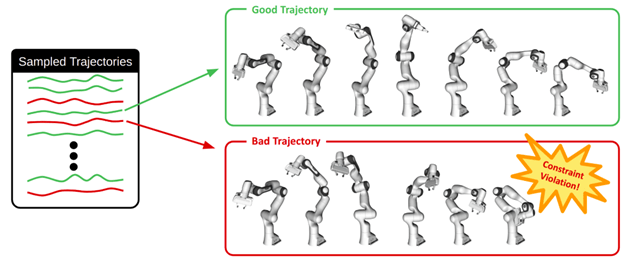
For a 7 degree of freedom (DOF) manipulator robot, bad trajectories may contain self-collisions.
Distributional Trajectory Sampling
In standard GP dynamics models, the posterior is represented in distributional form – using its parameters, the mean vector and covariance matrix. In this form, it is difficult to reason about
about the safety of entire trajectories. This is because trajectories are generated through iterative random sampling. Furthermore, this kind of trajectory sampling is limited to cases where the intermediate state marginal distributions are Gaussian distributed.
Pathwise Trajectory Sampling
Zwane uses an innovative alternative called “pathwise sampling” [3]. This approach draws samples from GP posteriors using an efficient method called Matheron’s rule. The result is a set of smooth, deterministic trajectories that aren’t confined to Gaussian distributions and are temporally correlated.
Adding Safety
The beauty of pathwise sampling [3] is that it has a particle representation of the GP posterior, where individual trajectories are smooth, differentiable, and deterministic functions. This allows for the isolation of constraint-violating trajectories from safe ones. For safety, rejection sampling is performed on trajectories that violate safety constraints, leaving behind only the safe ones to train the policy. Additionally, soft constraint penalty terms are added to the reward function.
Sim-Real Robot Experiments
To put this approach to the test, Zwane conducted experiments involving a 7-DoF robot arm in a simulated constrained reaching task, where the robot has to avoid colliding with a low ceiling. The method successfully learned a reaching policy that adhered to safety constraints, even when starting from random initial states.

In this constrained manipulation task, the robot is able to reach the goal (shown by the red sphere – bottom row) without colliding with the ceiling (blue – bottom row) using less than 100 seconds of data in simulation.
Summary
Sicelukwanda Zwane’s research makes incremental advances on the safety of simulated trajectories by incorporating safety constraints while keeping the benefits of using fully-Bayesian dynamics models such as GPs. This method promises to take MBRL out of simulated environments and make it more applicable to real-world settings. If you’re interested in this work, we invite you to dive into the full paper, published at the recent IEEE CASE 2023 conference.
References
By Sharon C Betts, on 18 November 2021
Welcome to the blog for the UKRI Centre for Doctoral Training in Foundational Artificial Intelligence.
Our aim with this blog is to inform the wider world of our research, ourselves and our ambitions in helping create new algorithms and foundational practices in artificial intelligence to help deliver the UK National Strategy in artificial intelligence.
Our CDT is one of 16 UKRI funded CDT’s focusing on artificial intelligence and building on the UK’s history of excellence with machine learning.
The UKRI CDT in Foundational AI sits within UCL’s Centre for Artificial Intelligence in the heart of London and helps bring together some of the best minds in the field of machine learning, natural language processing, robotics, deep learning and reinforcement learning (and so much more!)
We look forward to letting you know more about us and what we are doing to help forward the research in artificial intelligence and create new frontiers in research.