Skulls, subs, and selective laser sintering
By ucqnklo, on 14 July 2014
We hear a lot about 3D printing as the future of manufacture, but it’s also finding many applications in research.
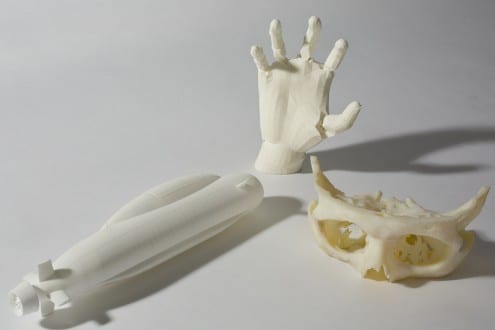
Today’s picture of the week shows three of the uses researchers at UCL Engineering are finding for additive manufacture.
On the left, a model submarine printed by a student in Naval Architecture lets them see their designs in 3D. In the middle, UCL computer scientists experiment with the exciting new problem of creating virtual models that can be printed out with movable, posable parts; and on the right, a section of 3D printed skull, recreated from scans by researchers at UCL Medical Physics based within UCLH, enables surgeons to plan their operations.

Just for fun: old school meets new tech: a chimp skull from UCL’s Bioanthropology Collections next to a high-tech 3D print of a modern human from UCL Medical Physics. Will 3D printed skulls be the future of anatomy teaching?
All of these models were printed using a method called Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). This is a kind of 3D printing that uses lasers to melt bits of a polymer powder together in the shape of a cross-section through the object you want to print. Then, a layer of power is added on top, and another layer melted. If it is resting on powder, that powder will just brush off when the plastic model is removed: if it is resting on a previously melted bit, it will stick to it.
This is a more expensive way to 3D print than the hobby-level 3D printers which are more commonly seen, which basically squeeze out layers of plastic like toothpaste, stacking them up into shapes . However, it allows the printing of more complicated shapes, with overhangs and interpenetrating parts – so it’s really handy for detailed research uses. UCL has a number of 3D printers, some free for all our staff and students to use in our open access Makespace.
Links
- 3D printing of non-assembly, articulated models – by Cali et al at UCL Computer Science
- Naval Architecture MSc at UCL
- UCL Medical Physics & Biomedical Engineering newsletter: article on ‘Facing up to disfigurement’ on pg 5
- UCL Institute of Making MakeSpace
 Close
Close