Blog Series – Breaking BEIS: Risks & Opportunities for Engineering Policy (2/4)
By laurent.liote.19, on 22 February 2023

This 4-part blog series covers the recent dismantling of the UK government’s department for Business, Energy and the Industrial Strategy (BEIS) and what it means for engineering policy. We take this opportunity to look at what we can learn from the creation and internal organisation of BEIS to reflect on how machinery of government changes affect engineering in and for policy. This blog series is written by final year PhD candidate Laurent Lioté, working on engineering advice for energy policy and part of STEaPP’s Engineering Policy Group.
Machining government: barriers and opportunities for engineering
Picking up where we left off last week, this post will cover how machinery of government changes can help or hinder the development of engineering advice for policy. This post looks at how BEIS came to be to understand the potential impact of the most recent reshuffle.
If you recall the diagram from last week, the energy and innovation portfolios have been bounced around frequently. Now the challenge with this type of machinery of government changes is that they lead to increased staff turnover (which is already quite high ‘by default’) and decreased knowledge retention, in turn breaking-up policy continuity.
Turnover happens at a high political level when new ministers come in like last week, in 2016 with the creation of BEIS or 2008 when DECC (the Department for Energy and Climate Change) was established. A less visible turnover however happens at policy levels where policy and technical teams (ex: DECC then BEIS’ engineering and science advice teams) get moved around depending on the portfolio and remit of the new departments.
This can easily result in a break in policy continuity as the ministerial remits are different, key individuals might leave (and with them some institutional memory), policy and technical teams have to find their footing, and advisers have to be brought up to speed on new policy areas. This last point is particularly important for technical policy areas, like energy, as new individuals don’t always have the tacit knowledge linked to corporate memory that enables them to assess the reliability of evidence. The lack of policy continuity can quickly become an issue when it comes to long-term challenges and targets like climate change policy.
But machinery of government changes are not always barriers to technical advice, in fact they can provide an opportunity for positive change like bringing a bit of engineering capacity back in-house (I might be biased!). When DECC was created for instance, the newly appointed CSA was clear that DECC’s mission of combatting climate change could not be achieved without hiring more engineers and scientists. In this case, a machinery of government change – and individual will and policy vision – increased the government’s engineering capability.
And in the end this question of policy vision and ministerial mission might be the key. How much engineering is recognised at the core of the new departments’ mission will determine how much engineering advice will be sought, deployed and used.
Looking at the aims of the two new departments, the technical (“energy supply, drive innovation”) is mixed with more economic imperatives (“growth, bills and inflation”). This is fine, lowering bills and creating jobs is important, but it does bring up the question of how much influence engineering vs. economics will have in policy – or if they are compatible. And that’s what we’ll cover in the next episode, stay tuned!
Blog Series – Breaking BEIS: Risks & Opportunities for Engineering Policy (1/4)
By laurent.liote.19, on 15 February 2023

This 4-part blog series covers the recent dismantling of the UK government’s department for Business, Energy and the Industrial Strategy (BEIS) and what it means for engineering policy. We take this opportunity to look at what we can learn from the creation and internal organisation of BEIS to reflect on how machinery of government changes affect engineering in and for policy. This blog series is written by final year PhD candidate Laurent Lioté, working on engineering advice for energy policy and part of STEaPP’s Engineering Policy Group.
February government reshuffle: plus ça change…
As of Tuesday 7th of February 2023, the UK’s Department for Energy, Business and the Industrial Strategy (BEIS) no longer exists… And as a researcher who has spent the last three years studying the ministry, this is important news! Rest assured the Prime Minister has not completely scrapped energy and business policy, BEIS has undergone what we call a ‘machinery of government change’ and its portfolio has been split between new and existing departments.
Before I launch into what the new ministerial organisation looks like and what the new remits are, let me say a quick word about what I got up to in the now defunct department. I am a final year PhD student, and my research has been focused on ethnographically studying engineering advice for policy at BEIS. Energy being an engineering demanding policy area, the ministry covering the topic seemed like a good site to investigate how engineering expertise is leveraged by the government. Through my research I have come to learn a lot about the history of the ministry and how its creation and internal organisation impacted its internal engineering capacity. This post and the next three in this series are therefore reflections on what we can learn from the more and less distant past to do ‘good’ engineering policy in the present.
So, back to the Prime Minister’s announcements. Last week BEIS portfolio was divided into:
- A new Department for Energy Security and Net Zero, tasked with “securing the UK’s long-term energy supply, bringing down bills and halving inflation”
- A new Department for Science, Innovation and Technology, who’s remit is to “drive innovation, improve public services and grow the economy”
- A combined Department for Business and Trade, in charge of “supporting UK business on home soil and abroad”
Now that might seem like a bold new direction for the UK government but to anyone who knows about the history of BEIS, this is actually more of a return to the roots. Indeed, BEIS was a merger of:
- The Department for Energy and Climate Change (DECC) and
- The Department for Business, Innovation and Skills (BIS)
Going even one step further, both DECC and BIS were spun off BERR, the Department for Business, Enterprise and Regulatory Reform. But rather than drown you in acronyms, I’ve compiled it all in one neat diagram:
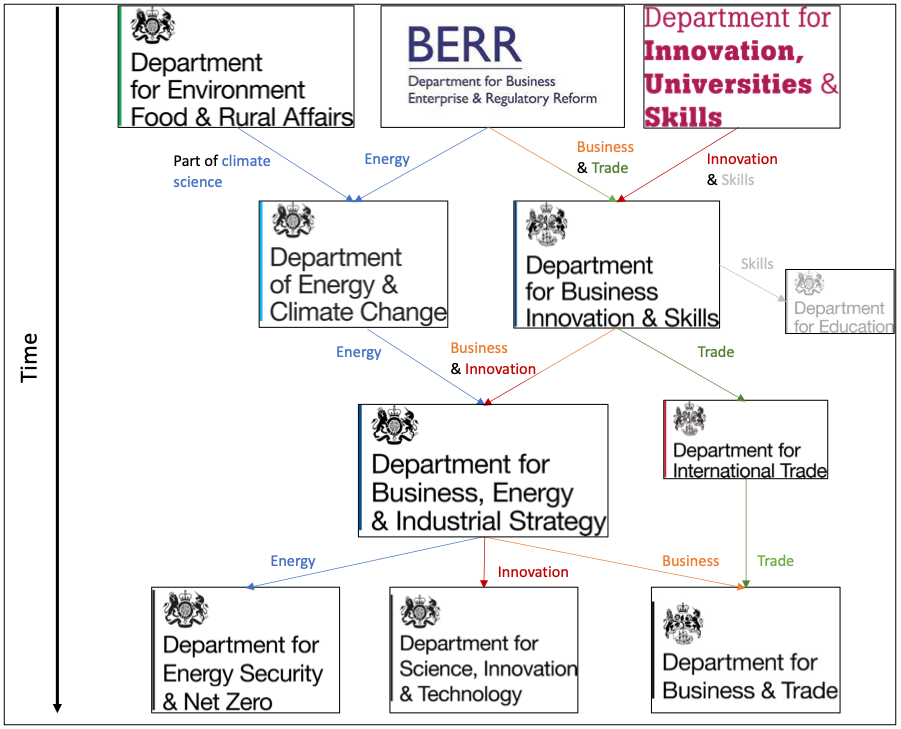
My point here, as you can see, is that this is all very cyclical. And given all those ministries have been focused in one way or another on energy and/or innovation, all those changes have had impacts on the government’s in-house engineering capacity in those policy fields.
This new reshuffle will have more than one policy professional say: “plus ça change, plus c’est la même chose” – but it’s not always the case, ministerial changes also provide windows of opportunity to change policy and institutional organisation. This is what I want to cover in the next three blogs by looking at BEIS and its history. How have machinery of government changes helped or hindered the development of engineering advice for policy? Is the current government’s focus on “growing the economy, reducing bills and halving inflation” going to be at odds with engineering advice? Is it finally time to push for engineering as an official ministerial remit or does science, innovation and technology cover it?
Find out in the next episodes of Breaking BEIS!
In the slums of Kampala, the phrase “survival for the fittest” takes on a whole new meaning: reflections from a recent field trip studying electricity access in Nakulabye slum, Kampala, Uganda
By penlope.yaguma.20, on 31 October 2022
By Penlope Yaguma
Penlope Yaguma is a 3rd year PhD student of Energy and Development Policy at the UCL Department of Science, Technology, Engineering and Public Policy (UCL STEaPP) and the UCL Engineering for International Development Centre (EfID). Her broad research interests are on electricity access in slums and informal settlements in African cities, with a specific focus on Uganda’s cities. Penlope’s work is inspired by her own experiences of growing up and living in Uganda, and she hopes to bring her formal training in electrical engineering and sustainable energy systems to understanding and creating solutions for the inequalities and injustices in service delivery and infrastructure provision in African cities.
“Everyone looks down on us because we live in the ghetto, but deep down they know that these ghettos are the heartbeat of Kampala.”

Despite slums’ close proximity to grid infrastructure or sometimes literally under the grid, accessing electricity in Kampala’s slums remains precarious, costly or downright unsafe
How it all began: In September 2022, I set out to do the fieldwork and field data collection for my PhD research in Nakulabye slum, one of over 60 slum settlements in Uganda’s capital Kampala. The plan was to conduct household surveys, hold focus group discussions in the settlement and interview key stakeholders on all matters electricity access specifically and access to social services and infrastructure more broadly. I was very fortunate to work with a passionate field team of geography students from Makerere University’s Urban Action Lab and the Centre for Climate Change Research and Innovation, and community guides who were residents of the settlement. We also received overwhelming support and assistance from the local council leaders (LC1s) of all nine administrative villages/zones that make up Nakulabye settlement. Many generously shared their experiences of securing social services for their jurisdictions and improving livelihoods for community members, families, and businesses. The devastating effects of Covid-19 and increasing cost of living are still being felt in Nakulabye, forcing some to close their businesses or pack up their families and move back to the village. Following two settlement walks, training and piloting the survey questionnaire, the actual data collection began – lasting about 2 weeks in total. In this blog post, I reflect upon this fieldwork exercise and write about my experiences and key observations.
PhD Episode III: The Rise of Engineering Advice
By laurent.liote.19, on 10 October 2022
Laurent Liote is a fourth year PhD student at UCL STEaPP. Follow him on LinkedIn (Laurent Liote), Twitter (@LaurentLiote) or ping him an email (laurent.liote.19@ucl.ac.uk).
Hi there, yes, it’s still me… and yes, I’m still working on my PhD! It’s been a few months since the last update so I figured I’d let you all know that, as promised, I’m working on the final part of my PhD trilogy (Episodes I and II can be found here and here, respectively). The overarching story arch, if you’ve missed the two previous instalments, is about understanding how engineering advice is deployed in energy policy practice. This post picks up where we left off, outlining what I’ve been up to since January and where I’m going next.

Carbon dilemma: Indonesia’s experience
By Muhamad Rosyid Jazuli, on 25 August 2022
The transition from fossil fuel-based to renewable energy has become one of the most important global issues at least in the past two decades. In Indonesia, however, incentives for renewable energy have decreased and in contrast, ones for fossil fuels have increased (Kompas, 22/6).
The alleged increase in this unsustainable incentive is encapsulated in a report by the International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD), titled Indonesia’s Energy Support Measures: An inventory of incentives impacting the energy transition, published this June.
During 2016-2020, the report states, that subsidies and compensation for fossil fuels in Indonesia reached 1,153 trillion Rupiah or around 65 billion Pounds. This number dwarfs incentives for other energy sources, for instance, 150 trillion Rupiah for renewable energy sources and 19 trillion Rupiah for electric vehicles and batteries.
Such gigantic spending indicates, unfortunately, that Indonesia is moving away from its commitment to building a low-carbon economy. At the Conference of the Parties (COP) 2009 and 2016, Indonesia committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 26% (with its own efforts) or by 41% (if receiving international assistance) by 2030.

Photo by Galen Crout on Unsplash
 Close
Close

