Young people against racism in 1980s London schools
By Erika Delbecque, on 9 January 2023
This post was written by Dr Shirin Hirsch, who was one of the 2022 UCL RIC Visiting Fellows.
Bengali lives are at risk whilst they are at Morpeth – we are punched, kicked and spat on. Enough is enough.
On a Monday morning in January 1986 one hundred Bengali students walked out of their secondary school in Bethnal Green, Tower Hamlets. That weekend they had drawn up a poster calling on all children to strike with them until their demands were met. In Oxford House just off Bethnal Green Road they set up an anti-racist alternative school. Three days later, the students returned to Morpeth with the school management agreeing to their demands. The strike was partially won. Young people, in taking action on their own behalf, had forced a change in the school.
Just over a decade later, I attended the same school. Bengali students were now a large part of the student intake and the school had new management. There were brief institutional histories given on dark days when fascists had attempted to organise and build their ranks inside the school. Then a new head teacher was brought in and it was said that he had transformed the school, later knighted for his efforts. But nowhere in these official histories were the actions of the students themselves remembered. Years later, when I stumbled upon a news report covering the strike, I was full of questions. Why did the students walk out of their school? Was the action connected to other strikes? What impact did the strike have on the school? And why had the students been forgotten for so long? I wanted to dig into the history of my old school, from a year before I was born, to try and find out more about where I was from and how young people had transformed their environment.
There are many challenges in researching the resistance of young people. For one thing, their lives are often remembered in words, documents or collections owned by adults. What is seen as ‘significant’ by older people might be different to young people’s views and experiences. Protests by young people are often against powerful institutions or people who can make decisions about what is and isn’t recorded. This was certainly the case in the Morpeth school strike, with the school management inviting ILEA press officers to the school to ensure the story was tightly controlled. Thames TV entered the school on the day the students returned from their strike but they were only able to interview selected staff and not students. That does not mean young people’s actions have been entirely erased. The local press did report on the Morpeth strike and documents from the strike were kept by a member of ILEA, which have since been donated to Tower Hamlets Archive.

Rally against racism in schools. Papers of Ken Jones KJ/4/1, UCL Special Collections, IOE Library and Archives, London.
Morpeth was not the only school where young people were struggling against racism. For my UCL Special Collections fellowship here, I have been spending time with two collections: the Marina Foster (MF) and Ken Jones (KJ) papers. Marina Foster was a Black teacher who had left South Africa as a refugee in the 1960s and in London became an advisory teacher at the ILEA for many years, focusing on multi-ethnic education and tackling institutional racism. Ken Jones was from the 1970s until 1990 a teacher in London secondary schools and active in the politics of education and in issues of curriculum, pedagogy and trade unionism. Both collections illuminate the debates, policies and projects on multicultural and anti-racist education taking place in London schools. There are documents that show imaginative ways of creating an anti-racist classroom, with teacher organisations like Campaign against racism in education (CARE) All London Campaign Against Racism and Fascism (ALCARF) as well as documents from ILEA (Inner London Education Authority).
The collections also illuminate the serious racism that existed in London schools. Daneford school, nearby to Morpeth, in Tower Hamlets, was the most publicised example of this and there are a number of documents on this in UCL special collections. The Guardian reported in 1986 that three quarters of the students at Daneford were of Asian origin and there had been a spate of racist attacks inside the school. The school gates were plastered with National Front stickers and posters, and a 12 year old Bangladeshi student had been viscously attacked with a razor blade by four white students. Another time, twenty white young people at a football match ‘spilled over into the school’ shouting viscous racist abuse. One teacher, Norma Hundleby, told the press: ‘Boys were coming out of all the classrooms to join them. It was totally out of control.’ Kumar Murshid, Chairperson of Campaign against racism in schools (CARS) explained that only ‘the dedication of the anti-racist teachers and pupils who have organised themselves against these attacks’ had helped to ease the tensions at Daneford. The racism, alongside the resistance, would receive national attention following the arrest of Daneford teachers and a school student who were protesting outside the Tower Hamlets ILEA office over the refusal of ILEA to take serious action against racism at Daneford school.
The reports at both Daneford and Morpeth schools challenged a version of schooling which saw young people as passive objects, who should simply ‘do what they are told’. Sajid, 18 years old, summed up the feeling when he explained to the press in 1986:
If we can’t go to school peacefully and study in safety, then we have to fight back. We have as much right as any white kid to go to school.

Black Parents Special no 1 (1985). Papers of Marina Foster MF/8/39, UCL Special Collections, IOE Library and Archives, London.
The voices of young people are sometimes hard to hear within these collections, but that does not mean they are completely silenced. In the Marina Foster collection there is a ‘Black Youth Annual Penmanship Awards’ with records of Black children’s writings from 1981, with essays on ‘What is means to be Black and British’ and ‘Being without Employment in Britain today’. The winning essay questioned the very nature of the school system, the student directly asking ‘does it prepare me or help me tackle the blatant and insidious forms of racism that, I am afraid to say, I will invariably encounter?’ The frustration at the school system, as well as wider society, was powerfully expressed by many of these young Black authors.

Gus, John (1986). The Black Working Class Movement in Education and Schooling. Papers of Marina Foster MF/8/63, UCL Special Collections, IOE Library and Archives, London.
The resistance at Morpeth secondary school in 1986 emerged out of this context and was not an isolated act. The Miners’ Strike had ended in March the previous year, a bitter defeat not just for the miners but for the whole of the labour movement. The year following the strike the numbers of days lost to strike action in Britain was at its lowest since 1967. However, school student strikes were not included in these figures. In April 1985 there was a national school student strike in response to the government’s attempts to make the Youth Training Scheme compulsorily for 16-17 year olds and to take unemployment benefits away from any young people refusing to participate. Alongside these strikes, the British government were openly attacking ‘hard left education authorities and extremist teachers’, as Thatcher put it. Parents were also resisting, and the Black Parents Movement, born in the 1970s, had begun to win serious changes in the schools. In 1981 and 1985 uprisings involving young people against the police had taken place in inner cities across England. Meanwhile teachers in 1985-6 entered disputes over cuts to schools and pay agreements. Gus John, a key activist and founder of the Black Parents Movement, in a speech he gave to teachers in 1986 which was later published as a pamphlet (M/8/63), explained:
The struggles waged by the black community outside of school and in relation to what was going on inside the school, gave school students the confidence to exercise their own power within the school. The school became for them the site of struggle against racism and against the treatment they were subjected to because of their class.
That relationship between students, community groups, teachers and wider political shifts is what I am interested in further exploring. This fellowship has given me the resources and time to piece together archival material and to explore these topics. I now hope to speak to some of the participants themselves. I am gradually trying to recover the resistance of young people against racism so as to remember and learn from their struggles.
The New Curators Project 2023 is Open for Applications!
By Vicky A Price, on 14 December 2022
The New Curators Project is an annual programme run by UCL Special Collections and Newham Heritage Month. It offers 10 young adults in East London the chance to develop the skills and experience needed to start a career in the cultural heritage sector.
What is Cultural Heritage?
The cultural heritage field is an area of work focused on preserving history and culture and making it available to the general public. Among other things, it includes:
Museums.
Arts organisations and charities.
Libraries and Archives.
Historic Buildings and heritage sites.
Archaeology.
What will the project entail?
Successful applicants will receive training from industry experts in key areas such as:
Carrying out historical research.
Using archives.
Creating an exhibition.
Running events.
Communications in the cultural heritage sector.
Participants will gain real work experience by creating an exhibition for Newham Heritage Month using historical material from UCL Special Collections, the Archives and Local Studies Library in Stratford and beyond.
The programme also offers employment support such as advice on applying for jobs, writing applications and being interviewed.
Participants who attend all the workshops will receive up to £550.
Who can apply?
Applications are open to people who:
Are aged 18 to 24 at the time of making their application.
Are living, studying or working in Newham, Hackney, Tower Hamlets and Waltham Forest.
Are not a university graduate or currently studying at university.
Have less than 6 months paid experience in the cultural heritage sector.
As this project is a part of Newham Heritage Month, there are 5 places available to individuals who live, work or study in the borough of Newham. The remaining 5 places are available to those who live, work or study in Tower Hamlets, Hackney or Waltham Forest.

New Curators Participants scrutinising an historical map.
When and where is it happening?
Workshops will be ‘in person’ on Tuesday evenings from 6pm to 8pm, beginning on March 7 2023 and ending June 27 2023. There will also be three full day workshops on Friday 31 March, Thursday 20 April and Friday 26 May.
Workshops will take place at the UCL’s brand new East London campus:
UCL East
One Pool Street
London
E20 2AF
Do applicants need to have any specific A Levels or GCSEs?
Absolutely not. We want to recruit participants who have a passion for local history, regardless of their qualifications.
How do I apply?
You can apply online via our online form. If you have difficulty using the form, please send us an email and we can find an alternative way for you to apply.
The application deadline is 8.00pm on Saturday 11 February 2023.
Delivered in partnership with Newham Heritage Month.
George Greenough’s papers – a window into the worlds of 19th-century science, wealth, and empire
By Kurt M Jameson, on 28 October 2022
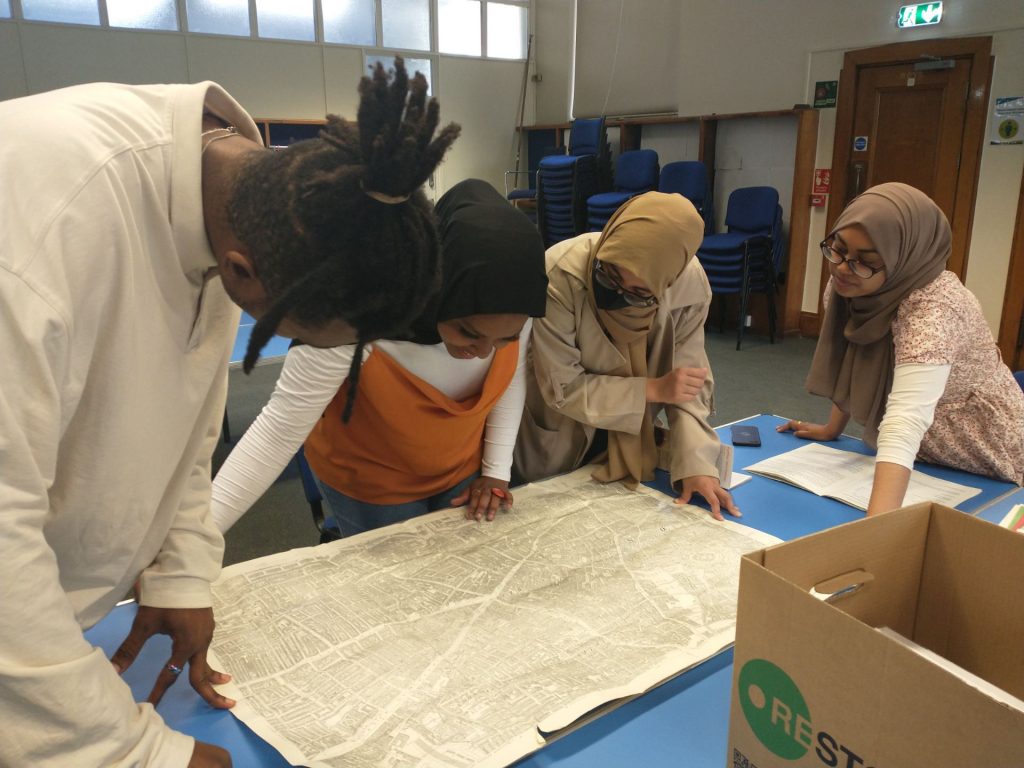
George Bellas Greenough inherited a fortune at the age of 16 and, as a rich man in his 20s, decided to devote his life to the study of geology. He is best-known for his Geological Map of England and Wales, published in 1820, which used new data and an innovative colouring system to highlight deposits of different types of rocks and minerals. He later became a controversial figure due to his clashes with William Smith, another geologist who had also made a very similar geological map at almost exactly the same time.
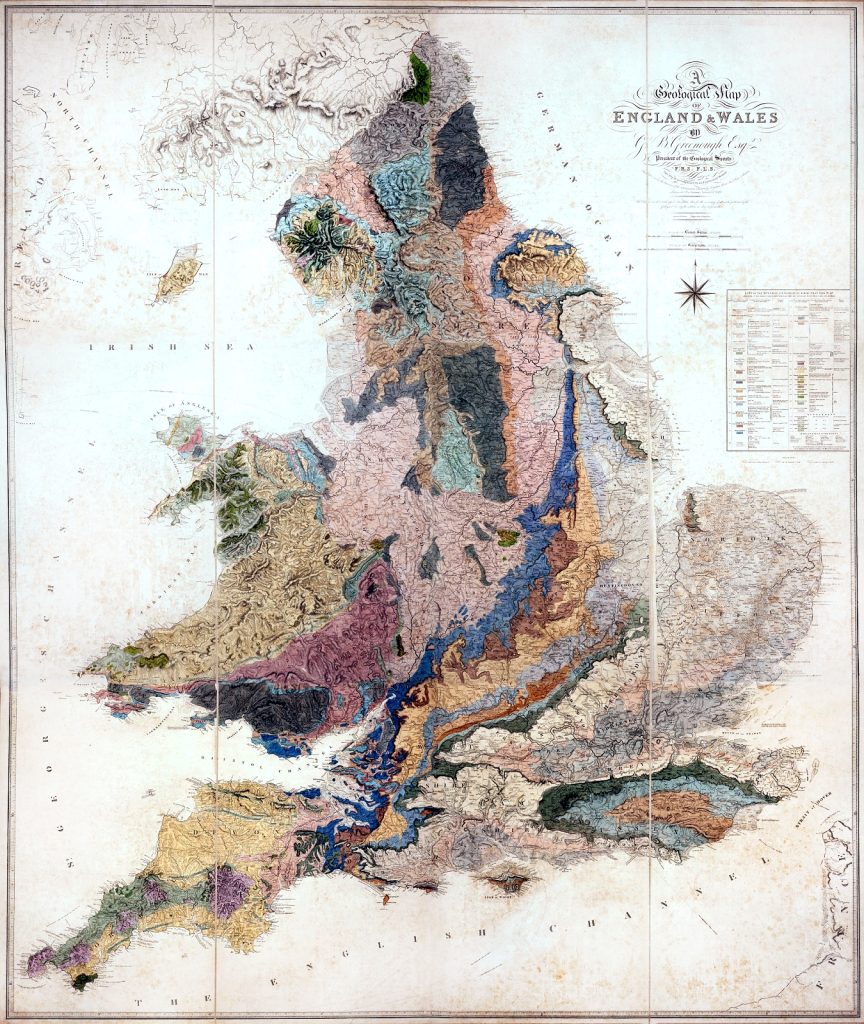
Greenough’s Geological Map of England and Wales, published in 1820 by the Geological Society. An original copy of his 2nd edition, published in 1839, is held at UCL Special Collections (GREENOUGH/A/2/1).
In the title of Simon Winchester’s book The Map that Changed the World (2001), he is referring to the map created by Smith. Winchester claims that Greenough plagiarised Smith’s map, and that Greenough was an elitist snob who blocked Smith’s entry to the Geological Society due to his class background. However, others have since argued that the creation of Greenough’s map was in reality more nuanced.

Portrait of Greenough by Maxim Gauci, mid-19th century. Held at the National Portrait Gallery.
Regardless of whether or not Greenough plagiarised Smith’s work, these maps were ground-breaking in the way that they displayed the minerals and resources that were lying under the ground. This was an exciting development not only for those with an interest in geology or the study of fossils, but also to those who stood to benefit financially. At the time, raw materials were in high demand in order to fuel the industrial revolution. In Simon Winchester’s words: “Landowners realized that they possibly had beneath their lawns, meadows and forests huge seams of coal that could make them rich beyond their dreams.”
This was also a time of a growing British Empire, which may explain why Greenough’s other major publication was a comprehensive geological map of ‘British India’, in 1855. Greenough produced this map with the help of the East India Company, but never visited the Indian subcontinent himself. Some of Greenough’s papers hint at the potential advantages for nations of having more accurate geological information. The following passage is from a draft letter of 1810 which appears to have been drafted or translated by Greenough for Jacques Louis, Comte de Bournon, regarding a collection of minerals that had recently been bought by the British Museum:
“The collection of the late Mr. Greville, celebrated throughout Europe, is now the property of Great Britain, a country the commerce manufactures & territorial revenue of which are intimately connected with the state of its mines & this acquisition has been made at a time when mineralogy engages a more than ordinary share of public attention.” (GREENOUGH/B/4/R/12)
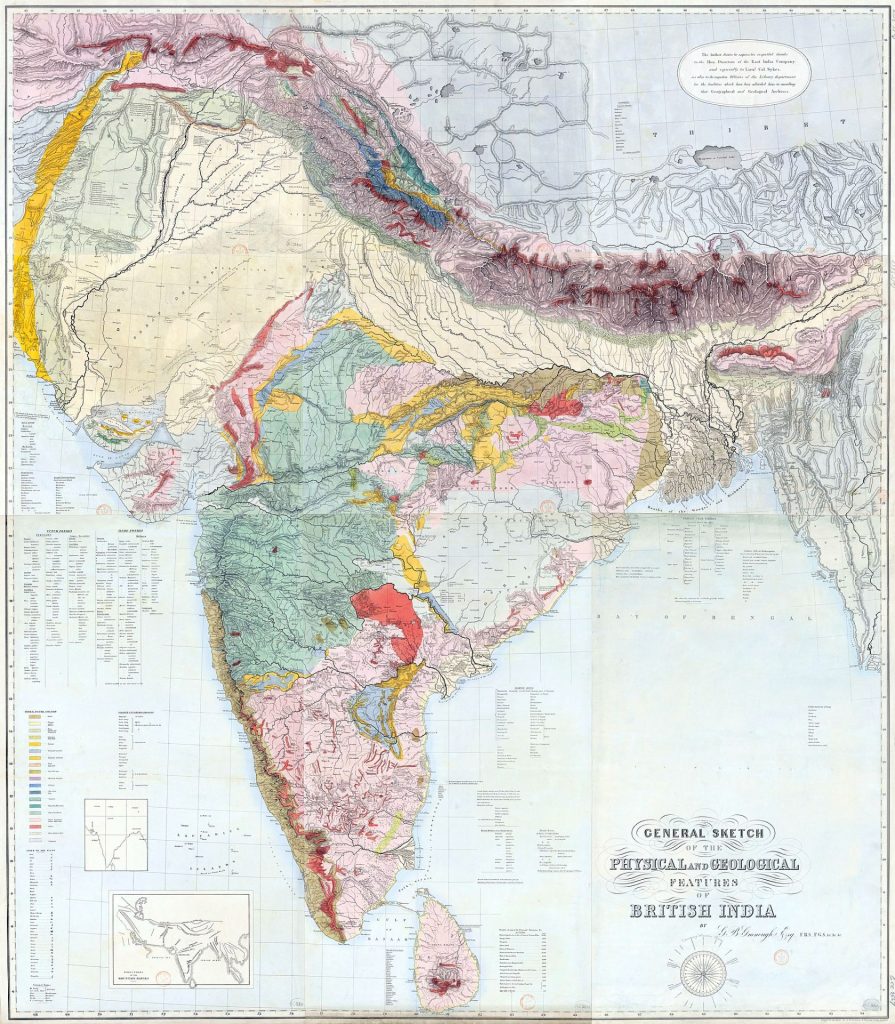
Greenough’s General Sketch of the Physical and Geological Features of British India, published in 1855. An original copy is held at UCL Special Collections (GREENOUGH/A/3/1).
UCL Special Collections holds a substantial collection of George Greenough’s papers. These papers include original copies and fragments of his own geological maps, his notes on various geological topics and debates, and his notes on other sciences. His diaries from his many expeditions through Europe include descriptions and sketches of the surrounding geology, as well as his observations on the local culture and politics. In one of these diaries he describes his escape from Sicily in 1803, as the French had invaded the Italian peninsula from the north (GREENOUGH/B/2/1/1).
A considerable amount of these papers consist of Greenough’s private correspondence. These letters read like a ‘who’s who’ of the elite scientific community in 19th-century Britain, and include letters from Michael Faraday, Francis Beaufort, Marc Isambard Brunel, and John Herschel. Being from this time period Greenough’s correspondence is almost entirely with other men, although there are some letters from women. In one letter Sarah Frembly appealed to Greenough to use his influence with the Admiralty, as her husband John had been shipwrecked and dismissed from the Royal Navy, leaving her family destitute (GREENOUGH/B/4/F/14).
In later life Greenough also focussed on the field of geography, serving as the President of the Royal Geographical Society from 1839 to 1841. This likely explains why he was in possession of a leaflet for a rescue mission for Franklin’s lost expedition to find the ‘Northwest Passage’ through the Canadian Arctic (GREENOUGH/B/3/5/1), and of prospectuses for the construction of a ‘Grand Georama’ in London (GREENOUGH/B/1/10).
The Greenough papers arrived at UCL in two separate deposits, the second deposit of which (‘Part B’) is newly-catalogued. The catalogue for the Greenough papers can be browsed via the UCL Archives online catalogue: https://archives.ucl.ac.uk/CalmView/. The Greenough papers will be of particular interest for any researchers of the history of geology, but may also prove useful for research into other aspects of 19th-century Britain.
To make an appointment to view any of the papers in the Greenough collection, please contact us at spec.coll@ucl.ac.uk.
“We Are Not Alone”: Legacies of Eugenics in Education and Society
By Nazlin Bhimani, on 17 October 2022
This post has been co-authored with Professor Marius Turda.
The IOE Library has on display a shortened version of the exhibition “We Are Not Alone”: Legacies of Eugenics which was first shown at the Weiner Holocaust Library in 2021 and which is now at the Royal College of Psychiatrists. The exhibition was curated by Professor Turda (Oxford Brookes University) with some content from UCL Special Collections (Galton Laboratory Collection and the IOE Library’s History of Education Collection) as well as content from the LSE’s Library. Following the opening of the exhibition, the Weiner Library hosted a Roundtable Discussion where all who worked on the exhibition shared our research. Both Indy Bhullar, Curator for Economics and Social Policy at the LSE Library, and I were subsequently invited by Subhadra Das (previously Curator of Science Collections at UCL Culture and now an independent scholar) to publish this research as short stories for the Wellcome Collection. The following provides some background on eugenics and the resources that are currently on display at the IOE Library.

The title of the exhibition, “We are Not Alone” is inspired by a widely circulated Nazi eugenic poster from the mid-1930s. After the introduction of the 1933 ‘Law for the Prevention of Hereditarily Diseased Offspring’, Nazi propagandists claimed that their eugenic programme of forced sterilisation was in no way different to provisions already existing in the penal legislation of countries such as the USA and Sweden, and which was about to be introduced in other European countries such as Britain, Hungary, and Poland. ‘We are not alone’, they said, hoping to garner international support for their plans to eliminate ‘defectives’ from society and to ‘purify the race’.
Eugenics was a global movement. The exhibition highlights this aspect, providing historical examples from Britain, USA, Italy, Sweden, and Romania, whilst recognising that eugenics programmes targeting individuals with mental disabilities and ethnic minorities were not stopped after 1945. They continued during the post-World War II period in countries as diverse as the USA, Scandinavia, Japan, Czechoslovakia, and Peru. The exhibition aims, therefore, to offer a historically informed account of our eugenic past, present, and future, balancing various elements of continuity and discontinuity, of idiosyncrasy and similarity between eugenic movements across the world.
The internationalisation of eugenics reflected a general appreciation in many parts of the world that science was the sufficient and necessary foundation for the long-awaited renewal of the human race. As a self-styled scientific theory of human betterment and planned breeding, eugenics was based on the principle that people who were deemed socially and biologically ‘unworthy’ of reproduction should be excluded. In the name of future generations, eugenicists dissolved aspects of the private sphere, scrutinising, and working to curtail reproductive, individual, gender, religious and indigenous rights. The boundary between the private and public spheres was blurred by the idea of public responsibility for the nation and the race, which came to dominate both. In the twentieth century, the state and the society at large increasingly adopted a eugenic worldview, even though none of it was based on proven scientific arguments. Instead, eugenics relied on speculations about social norms, cultural, ethnic and gender differences, and racial worth. Ideas of economic and social productivity also flowed readily from eugenic arguments, and eugenicists argued that if an individual was found to be socially ‘unfit’, it was appropriate for them to be ‘weeded out’. ‘Unfit’ had become a label for those members of society who were deemed ‘pathological’, ‘criminal’, ‘asocial’, ‘foreign’ and ‘undesired’.
Eugenicists claimed to act in the name of future generations by ensuring the continuity of people who were believed to be ‘hereditarily healthy’. Some eugenicists highlighted the primacy of heredity in shaping character and behaviour, while others insisted equally on the role of education and the environment. Not surprisingly, they also disagreed over which eugenic measures were deemed practical and efficient, and which ones should be rejected on ethical, scientific and religious grounds. In Britain, for instance, the Eugenics Society set up a committee to draft a sterilisation bill in 1929, chaired by the society’s president, Bernard Mallet. Two years later Major Archibald Church (1886–1954), a Labour MP and member of the Eugenics Society, introduced a sterilisation bill in the House of Commons, but it was rejected. One of his Labour colleagues, physician Hyacinth Morgan (1885-1956) rebuked the bill sharply: ‘Some when inebriated see beetles; the eugenist intoxicated, sees defectives’. In 1932, another sterilisation committee was established under the chairman of the Board of Control, Lawrence Brock (1879-1949). But these efforts led nowhere, as no sterilisation bill was introduced in Parliament again.
The exhibition presents us with the opportunity to review how assumptions and attitudes rooted in eugenic principles became entrenched in British education. From the beginning, eugenics appealed to educationalists, school reformers and feminists who advocated teaching the nation’s children and the youth ‘sound morals’ alongside physical education and modern ideas of hygiene. These were considered prerequisites for maintaining a healthy body and mind, and in society’s advancement towards a eugenic future. Educationalists such as the co-founder of the London School of Economics, Sidney Webb (who was instrumental in the establishment of the London Day Training College –now the IOE, UCL’s Faculty of Education and Society), was a key supporter of eugenics. Other examples include heads of colleges such as Margaret Tuke, Principal of Bedford College and J. J. Findlay of Owen’s College, Manchester, the London County Council’s Schools Inspector, W. H. Winch, and the educational psychologist Cyril Burt.
The cases display the intelligence tests or IQ tests from the Psychology and Human Development (PHD) Collection at the IOE. These tests were adapted by Cyril Burt from the IQ tests developed in Paris by Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon at the turn of the twentieth century. Burt’s ‘mental footrule’ was used to rate the intelligence of a child and his evaluation of mental deficiencies influenced the outcome of the 1924 Hadow report on psychological testing and the 1929 Wood Report of the Mental Deficiency Committee and the Board of Education. The latter recommended the reclassification of children considered to be ‘mentally defective’ . Also on display are publications by the experimental psychologist, H. R. Hamley and director T. Percy Nunn on The Education of Backward Children: and, Juvenile Delinquency in England and Wales as well as A Textbook of Hygiene for Training Colleges by Margaret Avery, Vice Principal of Warrington Teacher Training College.

Besides focusing on biological hygiene, Avery devotes an entire chapter on eugenics. This chapter provides examples of how eugenic thinking persists in the present day and is consistent with recent statements made by some politicians currently in power. For example, Avery states that while there are many ‘causes of pauperism’, one of them is that the working classes simply ‘lack…”grit”‘(p. 310)–a message that is not dissimilar to the one recently expressed by the (now previous) prime minister in relation to ‘British workers being the worst idlers in the world’. In relation to immigrants, Avery states: ‘We should welcome the right type of immigrant and discourage the wrong type’ and ‘we… receive the off-scourings of other countries, and these are racially very undesirable’ (p. 320). Once again, this mirrors the views of the present government on refugees and immigrants. Avery ends her chapter by stating that Christianity is on the side of the eugenicists because it, ‘more than any other power, has given us a sense of the infinite value of human life, and the eugenicist is trying to prevent the wreckage of human life’ (p. 323). While the Church has spoken out against these messages in Britain, the story is far from different in the United States (see Witnessing Whiteness by Kristopher Norris). Avery’s book continued to be published in several editions until 1951. It was the recommended textbook for the Board of Education’s teachers’ examination in hygiene. Undoubtedly, it will have influenced the thinking of generations of teachers and their students.
RIC Visiting Fellows appointed
By Erika Delbecque, on 3 October 2022
UCL Special Collections and the UCL Research Institute for Collections are delighted to announce that we have appointed two inaugural RIC Visiting Fellows. The Fellowship programme is an opportunity for external researchers to visit UCL for up to six weeks to conduct research on a topic centred on our holdings of archives, rare books, and records.

Dr Shirin Hirsch
Dr Shirin Hirsch will be working on a project called Young people against racism: School-student strikes and 1980s London Schools. She will be using the Ken Jones and the Marina Foster archives to explore the active role of school-students in the construction of anti-racist policy and practice in 1980s London schools.
Dr Hirsch, a Senior Lecturer in History based jointly at Manchester Metropolitan University and the People’s History Museum, is a specialist in histories of race and resistance in Modern Britain. She is in the early stages of writing a book on anti-racism in post-war British history with a focus on resistance from below, which her research at UCL Special Collections will support.
Focusing on items from the Graves Library collection, Dr Yelda Nasifoglu will study the circulation of mathematical works in Britain up to c.1700 for her project entitled Reading and Collecting Mathematics in Early Modern Britain. She will examine early modern book catalogues and individual copies from our collection to gain more insight into the mathematical book trade of this period.
Dr Nasifoglu is an historian of early modern mathematics and architecture, and an Associate Member of the Faculty of History, University of Oxford. She obtained her Ph.D. from McGill University for her dissertation entitled ‘Robert Hooke’s Praxes: Reading, Drawing, Building’, in which she studied shared practices in the scientific and architectural work of the 17th-century virtuoso Robert Hooke (1635–1703).
The Fellows will be visiting UCL in October and November of this year. During this period, they will participate in the programme of workshops, talks and lectures run by the RIC and UCL Special Collections. The events will be advertised on the RIC website and the UCL Special Collections Twitter feed.
Digitising the Annual Reports of the Institute of Archaeology, Volumes 1-13 (1938-1958)
By Vicky A Price, on 15 September 2022
This blog was written by Katie Meheux.
Volumes 1-13 (1938-1958) of the Annual Report of the Institute of Archaeology (formerly University of London, now UCL) have been digitised and made available as an open access resource through UCL Digital Collections and the Internet Archive following a project initiated by the UCL Institute of Archaeology Library and funded by UCL Special Collections.
The Annual Report was the Institute’s first annual journal, a tradition still continued today by Archaeology International. Each volume combined administrative information with academic research articles. Administrative reports outlined teaching, outreach, exhibitions, projects, excavations, collections, and lectures from visiting scholars – all the Institute’s day-to-day activities and a snapshot of its students, who came from all over the world. Research articles highlighted the international archaeological interests of the Institute’s staff – not just the academics, but librarians, photographers, and technicians too. Students also contributed research articles in a tradition now continued by Papers from the Institute of Archaeology.

The Institute of Archaeology volumes – in need of conservation and looking their age.
The Report was the first journal produced by a university archaeology department in the UK and forms an important research resource for the history of the Institute of Archaeology and archaeology as an international discipline. Like all archaeological journals, the Report reflected and absorbed changes within the wider discipline and as such, charts key developments and changes in archaeological practice during the twentieth century. Volumes also allow us to see how the Institute chose to present itself to the contemporary British academic community and its wider public audience.

Contents page of the first volume of Annual Reports of the Institute of Archaeology.
The COVID pandemic, which caused extended periods of closure and limited access to libraries during 2020 and 2021, highlighted the problems of retaining such a valuable research resource as print only. There was also a conservation imperative behind the project; to protect the fragile print copies held by the Institute library. The Annual Reports join other open access Institute of Archaeology resources, notably the Gordon Childe Skara Brae Notebooks (1928-1930), digitised as a joint project with Historic Scotland. British archaeological societies and organisations have been making historic journal content available for over twenty years, both independently and through the Archaeological Data Service (ADS), the leading digital repository for heritage data in Britain. Digitising historic journals means they can be used in new ways; for example, Gwynedd Archaeological Trust volunteers have been using open access historical journals to enhance the regional Historic Environment Record (HER) for north-west Wales.
Although print copies of the Reports can be found in libraries world-wide, providing online access will assist researchers, students, and the public and help to raise awareness of the rich and significant history of the Institute of Archaeology. Digitising the journal will broaden access for scholars, students, and the public, raise awareness of the rich and significant history of the Institute of Archaeology, and protect an increasingly fragile ‘in demand’ print resource for the future.
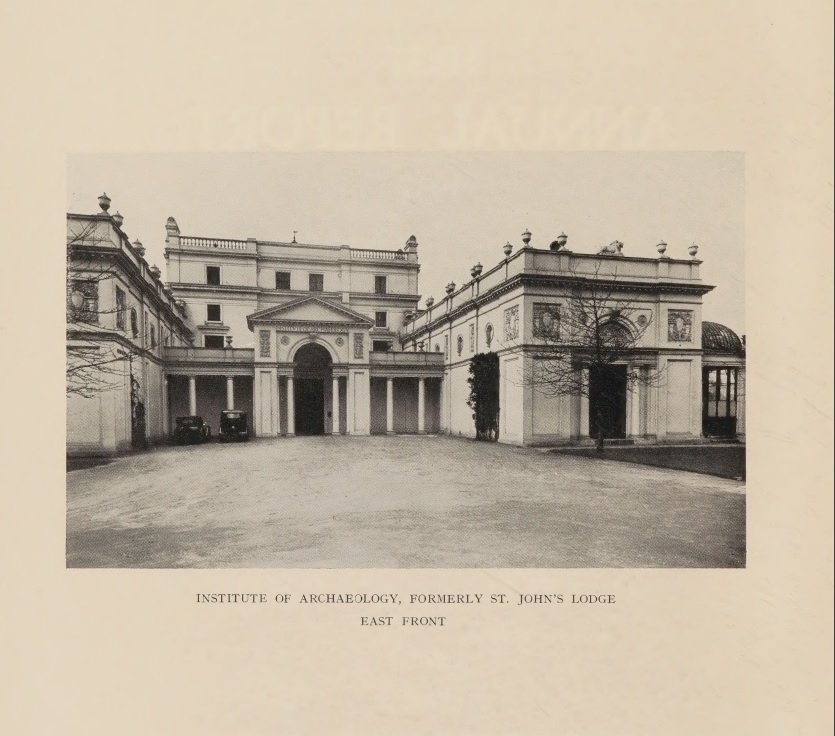

A picture of the Institute of Archaeology at St Johns Lodge – the frontispiece of the first volume.
Liberating the Collections 2022: A Volunteer’s Experience of Searching UCL Special Collections
By Erika Delbecque, on 23 August 2022
This guest blog post was written by Jane McChrystal , who spent five months volunteering at UCL Special Collections as part of the Liberating the Collections project.
In March I was presented with an exciting opportunity – discovering the work of women authors published before 1750, held by UCL Library’s Special Collections. I’d been invited to join a team of volunteers for the library’s Liberating the Collections project, by Head of Rare books, Erika Delbecque. Next, Erika convened an online meeting to introduce volunteers to each other and some members of the library team. During the meeting the librarians showed us how to identify works catalogued in the Special Collections using the Explore service, knowledge which could then be applied to the pursuit of the individual projects Erika had assigned.
There were some initial qualms- what if there weren’t any works by women authors pre 1750 in UCL’s collections, or I couldn’t work out how to find them? Luckily, my supervisor, Jo Baines, Academic Liaison Librarian / Archivist, was at hand to reassure me that there were, as I’d hoped, many different ways of approaching the collections to find relevant texts, so it was fine, at this stage to try out a variety of search methods and see what worked.
Initially, I set out in quite a random fashion. I didn’t make much headway, but I was able familiarise myself with Explore and become more confident about finding my way round the collections. And then, Covid struck in April, leaving me quite foggy for a number of weeks.
Once the fog lifted, something had become clear, I needed a system. A simple idea occurred to me. How about approaching my searches with a list of women authors who lived between the 14th and 18th centuries? In this instance, Wikipedia was my friend and it helped me to compile a list of 353 authors. I then selected some who looked the most promising and noted the subjects they addressed, and the literary forms they employed, such as poetry, meditations or drama. Consequently, I was able to match the authors with the collections they were most likely to be found in and the carry out a simple author search in the catalogue of the relevant collections.

The title page of
Letters of the Right Honourable Lady M-y W–y M–e by
Mary Wortley Montagu (Dublin : Printed for P. Wilson, J. Hoey, Junior, and J. Potts, 1763). [SSEES Library, Rare Books Room, KMisc51]
Before my search, though, I wasn’t aware of her four other dramas and poetry, mainly composed of paeons of praise to various illustrious individuals and members of royalty. I really knew very little about this literary form, but as I went ahead with further searches, I came to realise how popular it was, which makes sense when you consider the important role of patrons in literary life at the time.
And then I came across a gem in the Rotton collection, a collection of Lady Mary Wortley Montagu’s letters to various eminent men in England, concerning her travels in Europe, Africa and Asia with her husband, a British ambassador, which lists the name “Mary Astell” among its contributors.
Mary Astell (1666-1731), sometimes referred to as England’s first feminist, was the author of A Serious Proposal to the Ladies for the Advancement of their True and Greatest Interest, a Lockean philosopher and the founder of a charity school for girls in Chelsea.
She also belonged to a circle of scholarly women in Chelsea, which included Lady Mary Chudleigh, Elizabeth Thomas and Elizabeth Elstob and Wortley Montagu. Each lived in quite different circumstances, ranging from the wealthy, aristocratic Wortley Montagu to Astell.
Astell was a single woman, whose family had fallen on hard times and, as such, had no prospect of marriage to a social equal. She survived on the patronage of women, like those in the circle, who shared her interests in feminism, the oppressive nature of marital relations and the importance of a good education for girls and women.
I returned to the catalogue in search of their names and found four other works by Montagu in the Rotton Collection, largely made up of more letters about her experiences in the different countries she lived in. It is fortunate that these letters were preserved in the eminent men’s libraries and published after their estates were distributed. These texts were then picked up by collectors who donated them to UCL Library.
So, what next? On 24th August I look forward to sharing my discoveries at a meeting of UCL Library’s Rare Books Club, where participants will have a chance to take a look at some of the texts I found and learn about the work of two fascinating women authors previously buried in the Special Collections, together with the stories of some other important women in their orbit.
All in all, these experiences of taking part in Liberating the Collections have lived up to every expectation I set out with and beyond. Working with Jo as my supervisor has been one of the most enjoyable of them and, thanks to her knowledge, flexible approach and supportive attitude, I found a path to these heroines.
Anthony Davis Book Collecting Prize 2022: results announced
By Tabitha Tuckett, on 22 July 2022
We are delighted to announce the winner and finalists of this year’s Anthony Davis Book Collecting Prize 2022.
The prize is open to students at London-based universities, and this year applicants included students from Birkbeck, Royal Holloway, SOAS, the Royal College Of Art and UCL.
A wide range of wonderful collections was submitted, but the panel had the difficult job of choosing a winner. Four applicants were shortlisted for the finals and presented their collections live to a panel of judges that included representatives of the Bibliographical Society, the Antiquarian Booksellers’ Association and the University Of London’s Senate House Library.

Items from ‘Swizzle And Serve’, the winning collection of Hannah Swan
Winner and finalists
The prize was awarded to Hannah Swan, studying for a PGDip in Archives And Records Management, for her collection entitled Swizzle and Serve: Party-Planning Books and Ephemera. She will have the opportunity to apply for the UK’s national collecting prize for students later this year.
Domenico Pino, studying for a PhD in History Of Art, was awarded an honourable mention by the judges for his collection of 19th-century Neapolitan books and prints entitled Bibliotheca Neapolitana.

Items from finalist Jessie Maier’s collection ‘The reclamation of Arab narratives in science fiction and graphic novels’
The other finalists were Jessie Maier, an MA student in Middle Eastern Studies, for her collection of graphic novels and science-fiction material entitled The reclamation of Arab narratives in science fiction and graphic novels and Małgorzata Dawidek, a PhD student in Fine Arts and Intermedia, for her collection of works on art, health and illness entitled Body Stories, with a particular emphasis on Polish publications.
All the finalists met with Anthony Davis and were given advice and contacts to support their future collecting. We’re delighted that Małgorzata, after being shortlisted, was awarded a grant from the Adam Mickiewicz Institute in recognition of her contribution to the dissemination of Polish culture by presenting her collection.

Items from ‘Body Stories’, the collection of finalist Małgorzata.
See the shortlisted students’ collections: 27 July and 10 August
All four candidates will be presenting their collections to the public in our UCL Rare-Books Club series over the next few weeks. Domenico and Małgorzata will present in person at the UCL Bloomsbury campus in London on Wednesday 27 July: book your place on Eventbrite and drop in any time between 12.30pm and 2pm. Hannah and Jessie will present online on Wednesday 10 August 1.05-2pm: booking opens soon on the UCL Rare-Books Club Eventbrite page.
Collectors of the future
We hope you’ll be able to come along to these events to support the finalists, but we’d also like to thank all the applicants and wish them good luck and many years of joy in their future collecting. Our thanks also go to the judges for generously giving their time and, most of all, to the benefactor of the award, Anthony Davis, for helping nurture the collectors of the future with his encouragement, expertise and enthusiasm.
The New Curators Project Visit Tower Hamlets Archives
By Vicky A Price, on 11 July 2022
This blog was written by Arzama Hossain, a participant on this year’s New Curators Project. The project seeks to offer a cohort of 18-24 year olds from East London the chance to learn more about the cultural heritage sector, receive relevant training and to produce something for a real life heritage audience as part of Newham Heritage Month. In Arzama’s own words, it is ‘a project in which you learn and work’ at the same time. This blog is a reflection that she wrote after visiting Tower Hamlets Local History Library and Archives.
Visiting Tower Hamlets Local History Library and Archives
Today I had the great pleasure to visit the Tower Hamlets Local History Library and Archives; I really had an amazing time exploring the place and the vast collection of artefacts they have. One thing I was pleased to learn was that anyone is able to visit them and it’s not an exclusive thing, this is a good thing as it allows people interested in history to be able to research some things at the source.
One of the things I enjoyed seeing was pictures of the local area throughout the year. I think it is important to keep an archive of photos which will allow people to see the history of the place they live. Due to the vast amount of material in the place, it feels like you are able to properly get an idea of local history and how it has progressed over the years. These archives are an important part of history as they showcase the important role of minorities in the history of this country and how they have helped make Britain what it is today.
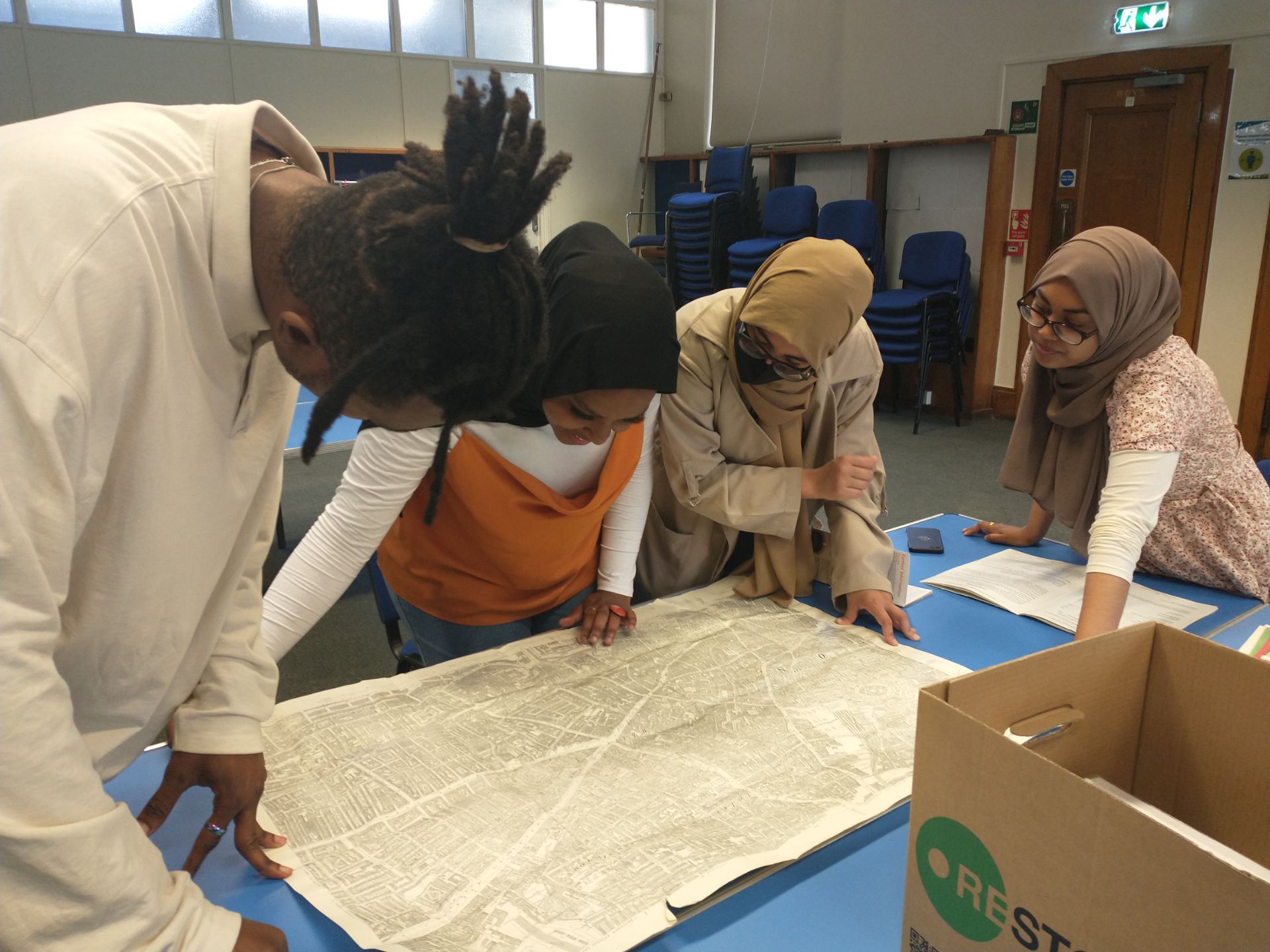

New Curators Participants scrutinising an historical map.
Archives play an important role in our understanding of the past, as they showcase some of the hidden aspects of history that many people may not know. Throughout history, only the biggest events got the spotlight while smaller, just as significant stories aren’t told as often. A country should always acknowledge even the bad mistakes of the past as it makes sure they don’t happen again, and keeping an archive of events allows people to learn the good and bad.
I moved to England from Italy when I was 12 and started learning about British culture but not forgetting my roots, seeing my community represented in the Archive gives you some inspiration to be like the people that came before you and made this country what it is. I wanted to learn more about the history of the Bengali people in London due to being Bengali myself and seeing them represented in the archives made me proud of my roots.
Archives are important things to have as they preserve important knowledge which otherwise may have been lost. People should take a trip and visit an archive as they are open for anyone to look at.
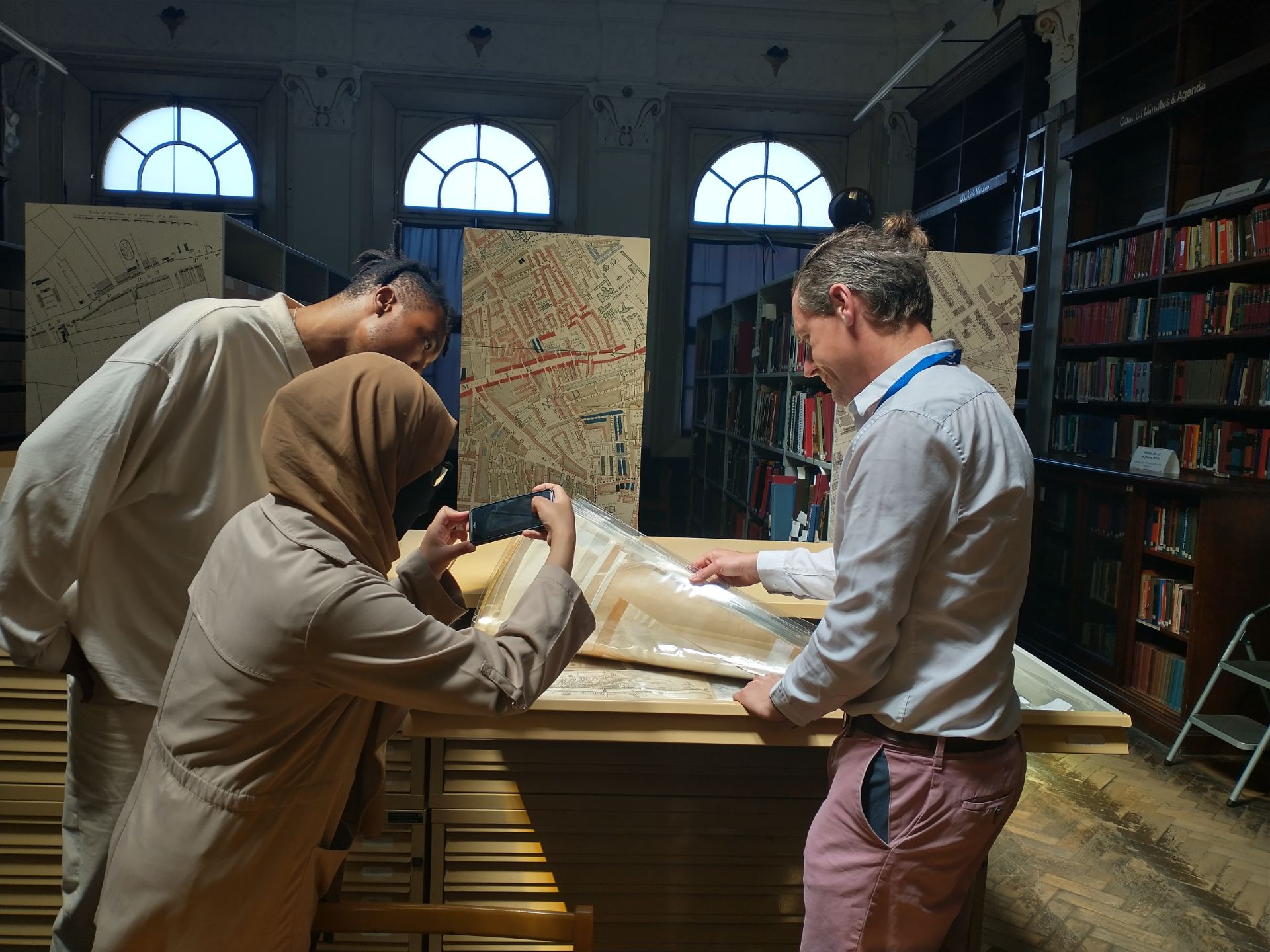

Archivist Richard Wiltshire shows participants archival maps and plans.
New Jewish pamphlets
By Vanessa Freedman, on 24 June 2022
The Hebrew & Jewish Studies Collections in UCL Special Collections include a treasure trove of material in the form of pamphlets. There are over 9,000 pamphlets on a wide range of subjects throughout the field of Jewish Studies, particularly Anglo-Jewish history, Zionism and liturgy. The pamphlets date from 1601 onwards, and are in English, Hebrew, German and a number of other languages.
In 2019 we completed a project to make these rich collections available to scholars and the general public. They are now catalogued in Explore, the most fragile items have been conserved, and a selection of them have been digitised.
We haven’t finished developing this collection though, as we are still acquiring pamphlets by purchase or donation. If you have any pamphlets that you would like to donate, please contact the Hebrew & Jewish Studies librarian.
Here are a few highlights from our recent acquisitions.
 One of the highlights of the pamphlet collection is a large number of orders of service for a variety of national and communal occasions. This particular service was a cross-communal event: published by the Office of the Chief Rabbi of the United (orthodox) Synagogue, those leading the service also included Rev S.J. Roco of the Spanish and Portuguese Synagogue and Rev Morris Joseph of the (Reform) West London Synagogue of British Jews. The occasion was a spate of attacks against Jews that took place in newly-independent Poland after the First World War. There were over 130 attacks against Jews in Polish territories between 1918 and 1921, causing around 300 deaths.[1] The Hebrew title Bekhi tamrurim means ‘bitter cry’.
One of the highlights of the pamphlet collection is a large number of orders of service for a variety of national and communal occasions. This particular service was a cross-communal event: published by the Office of the Chief Rabbi of the United (orthodox) Synagogue, those leading the service also included Rev S.J. Roco of the Spanish and Portuguese Synagogue and Rev Morris Joseph of the (Reform) West London Synagogue of British Jews. The occasion was a spate of attacks against Jews that took place in newly-independent Poland after the First World War. There were over 130 attacks against Jews in Polish territories between 1918 and 1921, causing around 300 deaths.[1] The Hebrew title Bekhi tamrurim means ‘bitter cry’.
A Palestine Munich? by R.H.S. Crossman and Michael Foot
 In this ‘provocative’[2] pamphlet, published in 1946, left-wing backbench MPs Richard Crossman and Michael Foot (later leader of the Labour Party) attack the Labour Government’s policy on Palestine. They criticise the government for indecision and compare the restriction of Jewish immigration in order to avoid Arab opposition to the pre-war appeasement of Hitler (hence the title). The pamphlet argues for the partition of Palestine to form a Jewish state and an enlarged Transjordan.
In this ‘provocative’[2] pamphlet, published in 1946, left-wing backbench MPs Richard Crossman and Michael Foot (later leader of the Labour Party) attack the Labour Government’s policy on Palestine. They criticise the government for indecision and compare the restriction of Jewish immigration in order to avoid Arab opposition to the pre-war appeasement of Hitler (hence the title). The pamphlet argues for the partition of Palestine to form a Jewish state and an enlarged Transjordan.
And finally, a fascinating oddity:
Teʻudah Yehudit = Idisher doḳumenṭ = Jewish certificate
 This ‘Jewish Certificate’, in Hebrew, Yiddish, English and Arabic, looks like a passport and includes space for the holder’s photograph, signature and personal details. It proclaims that ‘the bearer of this certificate is a Jew not a Zionist and has no connection with the nationalist movement which has gained control over the Holy Land and turned it into a Zionist state by falsely assuming the Jewish names of Zion and Israel’. It was produced in 1976 or 1977 by the anti-Zionist ultra-Orthodox group Neturei Karta, some of whose members refuse to carry an Israeli identity card[3].
This ‘Jewish Certificate’, in Hebrew, Yiddish, English and Arabic, looks like a passport and includes space for the holder’s photograph, signature and personal details. It proclaims that ‘the bearer of this certificate is a Jew not a Zionist and has no connection with the nationalist movement which has gained control over the Holy Land and turned it into a Zionist state by falsely assuming the Jewish names of Zion and Israel’. It was produced in 1976 or 1977 by the anti-Zionist ultra-Orthodox group Neturei Karta, some of whose members refuse to carry an Israeli identity card[3].
[1] Anna Cichopek-Gajraj and Glenn Dynner, “Pogroms in Modern Poland, 1918–1946,” in Pogroms: A Documentary History, ed. Eugene M. Avrutin and Elissa Bemporad (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2021), 193.
[2] Kenneth O. Morgan, “Foot, Michael Mackintosh (1913–2010), journalist, politician, and author,” in Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (2016).
[3] Menachem Friedman, “Neturei Karta,” in Encyclopaedia Judaica, ed. Michael Berenbaum and Fred Skolnik (Detroit, MI: Macmillan Reference USA, 2007).
Eighteenth-Century Digitisation At UCL
By Tabitha Tuckett, on 24 June 2022
This post was written by Caroline Kimbell, UCL Library Services
Allow me to introduce myself and ECCO: I’m Interim Head of Commercial Licensing and Digitisation, which involves working with publishers to identify rare books and archives for online publication, earning royalty income for the libraries, acquiring preservation images, free or discounted access to online resources and, after a suitable contractual period, allowing us to re-use digital content in any way. In a previous career in publishing, I worked on developing “ECCO” – Gale’s Eighteenth-Century Collections Online.
Working out how many books were published in the 18th century, in the English language or in English-speaking countries has been an ambition of the library world since 1977, and the current answer according to the English Short Title Catalogue (ESTC) is 351,689 held across 2,000 libraries.
You may imagine that this epic project was completed years ago, and that everything listed by ESTC would be available in ECCO or elsewhere? Not so.
For a few years now, a “final” tranche of digitisation has been in preparation to supplement ECCO’s current 180,000 titles. The “long list” for this third tranche currently stands at 78,000 titles. UCL is not an 18th century library, and when I arrived, I imagined that we would have little eligible material. I was wrong. We will be contributing about 320 items totalling around 66,000 pages, of which 59 have been accredited by ESTC as brand new entries – in other words, unique, first-time discoveries.
Many of these new finds are in UCL core subjects and include books on the volcanos of Sicily, agricultural enclosure, the structure of human teeth, works by Joseph Priestly and a Compleat History of Drugs from 1737. One among UCL’s thousands of eligible titles, inexplicably absent from Penguin Classics, “Human ordure, botanically considered” (1757), is already on ECCO but surely worth a mention?

Fig.1: The Ladies Astronomy And Chronology by Jasper Charlton (1738) UCL Special Collections GRAVES 15.c.6
Among female authors it is splendid to find An Essay on Combustion 1794 by Mrs Elizabeth Fulhame, “the first solo woman researcher in chemistry”, Mary Wollstonecraft on the French Revolution, the prolific Mary de la Rivière, or even a 4-part Ladies Astronomy from 1738, in which the Sun smiles approachably for female readers (fig.1)
We will also be contributing new-to-ESTC editions by major authors – Swift, Defoe, Pope, Beckford – astonishingly still coming to light in 2022. Our 1787 Mohawk language Book of Common Prayer is already online, but when it comes to travel and the exotic, we have real delights – such as new-to-ESTC, “Four letters concerning the growth of grape vines in the Island of Bermudas” from 1741 (worth a try), and a rare 1746 London edition of sci-fi novel A journey to the world under-ground by Norwegian satirist Ludwig Holberg (as in Grieg’s tribute Suite) for anyone who had ever wondered what a Baroque Dr Who monster might look like (fig.2).

Fig.2: A Journey To The World Underground by Nicholas Klimius [i.e. Ludwig von Holberg], translated by John Lumby (1742) UCL Special Collections STRONG ROOM E 224 H61
Unfortunately, data-combing our 18th century holdings against ESTC and the online landscape has revealed a backlog of wrinkles which are being addressed, in part by our wonderful placement student Ollie Nelmes: only 61% of our 18th century holdings were recorded on ESTC, but this project gives us a fantastic opportunity to refresh the collections, improve and enhance their discoverability and step forward as a rich repository of 18th century rare, and in some cases, unique books.
Remember 2012?
By Vicky A Price, on 24 May 2022
The New Curators Project is run by UCL Special Collections, in collaboration with Newham Heritage Month. It is an annual programme for young adults (aged 18-24) who are interested in working in the cultural heritage sector, whether that be the arts, libraries, museums or heritage sites. It aims to provide the training and experience required for these new professionals to take their first steps on their chosen career path, and to create an opportunity for the group to create work for a real audience as they take their first steps into this field of work.
Each year the cohort create something for Newham Heritage Month’s programme, based on the given theme. 2022’s theme is ‘What London 2012 Means to Us’, and so participants set about collecting oral histories, film footage and photography of the Olympic Park and surrounding area. This is their first short film, created in response to the theme.
Get to know 2022’s cohort and revisit this page for addition short films in the month of June 2022!
Q&A with Erick Jackaman, 2021 Anthony Davis Book Collecting Prize Runner Up
By Sarah S Pipkin, on 28 April 2022
Erick Jackaman very kindly talked to us about his experience applying for the Anthony Davis Book Collecting Prize and his fantastic collection ‘Read my Genders: A Trans for Trans Collection’. You can follow Erick on Instagram and Twitter @transingabout

Tell us a bit about yourself
I’m Erick Jackaman, a UCL alum. I was an MSc Digital Humanities student (2020/2021). I’m queer, trans, 23 and a Londoner. I’m passionate about trans representation and trans joy.
What collection did you submit?
I submitted my collection of transgender print materials, which I titled “Read My Genders: A Trans for Trans Collection”. At the time of submitting, it contained 69 items, ranging from fiction books to museum guides to event flyers to zines and more! In general, I prioritise self-published and limited edition print materials and I focus on work by trans people for a trans (and wider) audience.

How did you start collecting?
When I purchased my first trans book in 2013, I wasn’t conscious of starting a “collection”. At the time, there weren’t many trans works of fiction and I was really gripped by a book called Refuse by Elliott DeLine. I read the ebook (twice!) and then decided to purchase a physical copy so I could have it forever and lend it to other people in my life (which I did). After that, I just started accumulating ephemera from trans events I went to, like film festivals and panel discussions, and buying international publications, like FTM Magazine, online.
Do you have a favourite item in your collection?
It’s so hard to choose a favourite, but I really love the Museum of Transology exhibition guide. I had come across this guide twice before I acquired it while visiting the Museum of Transology in London and then in Brighton, but the guide belonged in the exhibition itself and wasn’t available for purchase. On my third visit to the collection, the curator, E-J Scott, was running around right before closing time and handed me a copy of the exhibition guide to keep. It was such a special moment!


Why did you apply for the book prize?
While reading about the prize, the phrase “print materials” really stood out to me because that’s exactly what a lot of my items are (rather than books). I thought it sounded like a really cool opportunity to actually take stock of my collection and present it to a wider audience. I honestly didn’t think I would win, but I thought – why not?
How did you find the application process?
I really enjoyed the application process because it made me actually write a list of all the items in my collection, which I hadn’t done before. I also loved spending so much time with my collection and thinking about the ways in which it could grow. That said, the application did take me many hours (mainly because I have so many items!)
Did the application process help you learn more about collecting?
The interview I had as part of the application (second round) was one of the most valuable chats I’ve ever had. I felt so lucky to have the attention of so many “book collecting professionals” and I learnt so much about how to store and preserve my collection. I feel very grateful for that!

How has your collection changed since applying?
Honestly, not much! I left the UK soon after applying and I am still travelling, so I haven’t been actively looking for new items. That said, I am currently in Singapore, which caused me to come across a beautiful and very meaningful book called Our Blood Runs Red Just Like Yours, which documents The T Project – “the first and only social service for the transgender community in Singapore”.
What advice would you give someone thinking about applying?
Go for it! If you already have that inkling that you have some sort of print material collection, do yourself the favour and spend time with your collection and submit an application! As for the application itself, even if you’re just starting out, demonstrate the clear “theme” of your collection and the direction you want it to grow – this part is important.
Thank you so much to Erick Jackaman for sharing about his collection and application! If you’d like to apply for the Anthony Davis Student Book Collecting Prize, you can learn more about the application on our website.
Applications are open to students at any London-based university who have a cohesive collection of print, manuscript, or ephemera items. The deadline for 2022 applications is May 3rd.
New Summer School at UCL: What does it mean to be a journalist in turbulent times?
By Vicky A Price, on 25 April 2022
University College London (UCL) Special Collections and the Orwell Youth Prize team up to offer one-of-a-kind Summer School!
Applications are now open for a very special Summer School at UCL in July 2022. Year 12s based in London are invited to join Special Collections and The Orwell Youth Prize to develop their investigative writing skills, encounter first hand stories of journalism from the past and present and meet present-day journalists who are at the forefront of their profession.
Up to 25 participants will attend a range of seminars, study sessions, writing workshops and trips that will shed light on the life of professional journalists. They will develop their own writing with support from professional journalists, who will offer advice and share their experiences. They will also learn how the work of one of the UK’s most famous journalists, George Orwell, has influenced modern day writing and thought. During the Summer School, participants will have access to Orwell’s original notes, letters and diaries in the UNESCO listed George Orwell Archive held at UCL Special Collections.

Year 12 participants at a previous UCL Special Collections Summer School.
The Summer School will take place for one week, from Monday 25 July to Friday 29 July, 10.00am – 4.00pm, and participants will be expected to attend every day.
Apply now to:
• Learn from the best; meet current day journalists who will share tips, techniques and stories from today’s real life news desks.
• Write your own journalistic piece, which will be published online by UCL Special Collections.
• Get hands-on experiences with original archive items from UCL Special Collections, including the UNESCO registered Orwell Archive.
This Summer School is suitable for a wide variety of students who are currently in Year 12 at a London state-funded school, particularly those interested in English, History, Politics, Language, Culture and Anthropology. Anyone applying should currently be studying at least one of these subjects at A level: English Literature, English Language, Politics, History.
This is a non-residential Summer School, meaning that participants will need to commute to and from UCL’s campus each day. Applications close at midnight on Sunday 12 June 2022.
If you have any queries about the Summer School or would like support with completing your application please email us at library.spec.coll.ed@ucl.ac.uk or call 07741671329.
Who are We?
The Orwell Youth Prize is an independent charity that sits under the auspices of the Orwell Foundation. It is a social justice-based writing programme rooted in Orwell’s values of integrity and fairness that introduces young people to the power of language and provokes them to think critically and creatively about the world in which they are living. The prize is driven by an understanding of social and educational disadvantage in the UK and works closely with schools and individuals to deliver an annual educational programme.
University College London’s Special Collections manages an outstanding collection of rare books, archives and manuscripts, dating from the 4th century to the present day. Together, the team preserve and conserve the collection and facilitate access through a reader service, academic teaching, digitisation and outreach. The Outreach programme aims to create inspiring educational activities for audiences who would not otherwise access the university’s special collections in UCL’s neighbouring and home boroughs; Camden, Hackney, Tower Hamlets, Newham and Waltham Forest.
Students Duke and Eric Reflect on their BA Education Studies Placement with the Outreach Team
By Vicky A Price, on 23 March 2022
We have been fortunate to host two students on a 50 hour placement from the IOE’s BA in Education Studies, and as their time comes to a close with us, they have written a blog to share their experiences. Both students spent time learning about the Special Collections department before immersing themselves in the delivery of an Outreach project at UCL Academy – an after school club called Illustrate! which explores the use of illustration in our collection of rare books, archives and manuscripts.
Eric Xu
As part of the IOE’s Education Studies Placement Module, my course mate Duke and I have been working with Vicky Price as part of UCL Special Collections’ outreach team on the after-school workshop: Illustrate. I had a keen interest not only in working with students in a visual art focused workshop, but also in the collection itself after seeing items from the Orwell Collection around UCL’s campus. Our placement began in early January when we met with Vicky for the first time online. As the weeks went by, Duke and I had the pleasure of becoming acquainted with the people and places of Special collections, and learning about the processes of archiving, cataloguing, digitisation and of course the outreach of the collection.
Our work on Illustrate began promptly in the first weeks, reviewing the past workshop deliveries, and taking inspiration from curated catalogues of the collection. Trying to come up with original ideas of how to integrate collection items into fun and fruitful activities for the students was definitely a challenge, but Duke and I were able to come up with and produce resources for sessions which we were keen to deliver ourselves. Creating these lesson plans and resources was a much more multifaceted task than I had anticipated, the considerations of how students react to your information and questions greatly influences and informs the direction of the class, and having Vicky help us with leading the direction of these disseminations was very helpful and eye-opening. Similarly with the resources and activities, I found that oftentimes I had to give the activity a go myself to determine the difficulty and viability of it for the class, which meant a lot of the times that I had to adjust or even change the resource entirely. Ultimately, the final product of the workshops we delivered were much different and more refined than the initial plans that Duke and I had drawn up.
Working with the students at UCL Academy was also an experience that has reshaped my perspective on professionalism in schools. There were many hurdles we had to hop, both expected and unexpected, including uncertainty with the number of students coming into the workshop. The students that did consistently come every week were lovely to work with, not only were they respectful and interested to learn, but they were also amazing at drawing. Trying to keep every student up to pace with one another and engaging all of them in the content was another struggle that Duke and I faced, and we realised that sometimes it’s impossible to have everyone interested or fully committed in participating, but again with Vicky’s assistance, the workshops still ran successfully.
Overall, the experience for me was an amazing and insightful experience into the organisational operation of UCL Special Collections, the preparation of workshops and resources as well as the teaching of students. I would highly recommend anyone interested to get involved, and I’m very grateful to have worked with Vicky and UCL Special Collections as part of my placement.

Drawing activity designed by Eric and Duke based on the sketch from the Penrose Papers (below).

A sketch of a ‘continuous staircase’, much like the work of Escher, taken from the Penrose Papers at UCL Special Collections.
Duke Li
This term, the placement module from BA Education Studies offered us an opportunity to be involved in the outreach team of UCL Special Collections and the project “Illustrate”. To be specific, the aim of the project was to give the knowledge of special collections items to an audience with a non-academic background. It was really great to bring out activities to the after-school club and have interactions with students on the topic of special collections.
Our experiences started with the introduction of the UCL Special Collections team. Before that, I didn’t know that the UCL Special Collection team involved so many departments. For instance, we took several visits to the UCL Science Library and “hidden rooms” in the IOE building in order to see parts of the collection. It is always exciting to see those rare collection items – archives, rare books, and manuscripts – especially in a storage space that adds a mystery to it. As the placement went by, we got to know how to search items in the Special Collections catalogue, learn about the digitalization of the special collections items, and the process of getting access to items in the reading room. We also had a chance to take a look at an exhibition of the collection. From my perspective, those activities helped me to get a better idea of how the UCL Special Collections team work and cooperates with each other, and the experiences that I got turned out to be helpful when conducting the “Illustrate” project in the later weeks.
As well as intaking this knowledge, we also managed to bring out two sessions to the students on topics related to the collection items. The “Illustrate” project was an after-school class for the students, but the participants all engaged and learned from the discussion and the drawing activities in their own ways. Most of them were really active and willing to interact with us. It’s really delightful when giving out sessions and making students involved in the class. Though the teaching experience was wonderful, we do have several aspects to reflect on.
1. The teaching experiences
In the first session, we designed the whole activity on the work of Escher and his impossible world. We also set questions to ask the students. However, since we didn’t notice the difficulty and the linkage between questions, some of the students may have felt it hard to follow these ideas. From this, we concluded that the questions should be more carefully designed to express less in-depth, but easy-to-follow ideas, or else the knowledge of the collection items can not be promoted. Luckily, the final outcomes of the drawing activities turned out to be a big success, due to the creativity of the students. They have their own designs and thoughts.
2. The external factors
We also encounter some problems with the project as a whole. Since the project was an afterschool class in the school, schools may pay less attention to our project than the school’s wider teaching and learning activity. This may be the reason that most of the time, we did not have a lot of participants for our sessions. Also, we experienced once that the school was closed due to a problem with their water supply, but we only find out that when we arrived there, so these factors may have affected the teaching quality as well as the experience of teaching and learning.
To conclude, the whole placement experience is really great, we got the chance to know the UCL Special Collection team and how a team like this operates. The teaching experience with students was always nice since they were all really engaged. Also, we were really interested by the idea of the outreach team’s work when we were trying to make linkage between the non-academic audience and the special collection items that deserve to be noticed by more people. It was a really nice experience and I learned and reflected a lot.
 Close
Close