Persistent Identifiers 101
By Kirsty, on 27 July 2020
You might have heard the phrase ‘Persistent Identifier’ or even PID in passing, but what does it actually mean?
“A persistent identifier (PID) is a long-lasting reference to a resource. That resource might be a publication, dataset or person. Equally it could be a scientific sample, funding body, set of geographical coordinates, unpublished report or piece of software. Whatever it is, the primary purpose of the PID is to provide the information required to reliably identify, verify and locate it.” – OpenAIRE
These identifiers either connect to a set of metadata describing an item, or link to the item itself.
In 2018, the Tickell report was released. It presented independent advice about Open Access, which had implications for the world of PIDs. Adam Tickell recommended that Jisc lead a project to select and promote a range of unique identifiers for different purposes, to try and limit the amount of confusion and duplication in this area.
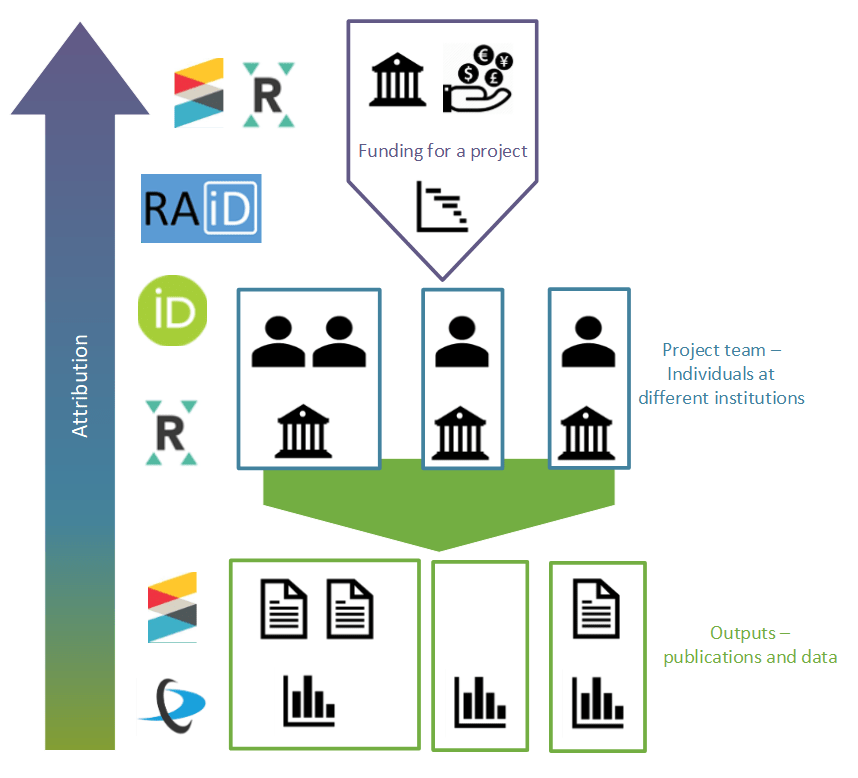
The JISC project has been in progress for the last year. They are working on what they describe as ‘priority PIDs’ which cover the following categories:
- People
- Works
- Organisations
- Grants
- Projects
So what are the PIDs we need to be aware of?
People
The primary PID for people is one that you will already be familiar with if you are a regular reader of the blog. Even if you aren’t, you have probably heard of it – it’s ORCID.
ORCID is an open identifier for individuals that allows you to secure accurate attribution for all of your outputs. It also functions quite nicely as an online bibliography, and can be used to automatically collect and record your papers in RPS. All in all, it’s pretty useful!
If you want to know more about what you can do with ORCID, have a look at our recent blog post ‘Getting the best out of your ORCID’. All of the details about linking ORCID to RPS and vice versa, are available on the blog and the Open Access website.
Works
The next identifier is for works. It’s another that you have probably seen, even if you don’t know a lot about them: DOI. DOI stands for Digital Object Identifier. It’s a unique registration number for a Digital Object. This could be an article or a dataset, but it could equally be an image, a book, or even a chapter in a book. DOIs are unique and persistent which means that if your chosen journal changes publisher, you will still be able to find your article because the DOI is independent and will keep up to date.
DOIs are most often acquired through a Registration Agency called Crossref, but you will also come across DataCite. Both of these services do the same job, providing and tracking DOIs, but the underlying tools are slightly different.
Did you know: if you have the DOI of a paper, an easy way to find that paper is to add https://doi.org/ to the front. The URL this creates will take you to the paper, no matter who published it. For example: 10.1080/08870446.2019.1679373 is a DOI, and https://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2019.1679373 will take you straight to the paper.
Organisations
The Research Organisation Registry (ROR) is a new PID registry that is being created by key stakeholders, including Crossref and Jisc, to bring more detail and consistency to organisational identifiers. The definition of organisations goes beyond institutions like UCL to include any organisation that is involved in research production or management, so this can include funders, publishers, research institutes and scholarly societies.
Grants
Crossref is key in the identification of individual funders and in creating identifiers for research grants. Grant IDs are DOI’s, but connected to grant-specific metadata such as award type, value and investigators. The intent is for funders to register each grant and provide a GrantID, which has the potential to make tracking papers and data linked to individual projects much simpler in the long run. Several hundred grants have been registered already, mostly via Wellcome. (With thanks to Rachael Lammey for the clarification 03/08/2020)
Projects
The Jisc project is supporting Research Activity ID (RAiD), a project based in Australia which creates a unique identifier for a research project. The intent is for this to be the final part of a network of identifiers that will allow people, works, and institutions to be linked to their projects and funders. This will complete the chain and allow accurate attribution and accountability at every stage of the research process.
How can I get involved?
The work being undertaken to select and support individual PIDs at each stage of the research process is a good idea, and if it works then it will be a step towards a fully interconnected, open and transparent research process. The next stage of the Jisc project is currently underway, and they are surveying all sectors of the UK research community about awareness, use, and experience of PIDs. If you want to contribute, their survey is open and has just been extended until 21 August!
2 Responses to “Persistent Identifiers 101”
- 1
 Close
Close



Hi Kirsty, Nice guide! But a DOI isn’t necessarily an Identifier for a Digital Object. It’s a Digital Identifier for an Object. That object can be physical, digital or abstract. See FAQ 6 at https://www.doi.org/faq.html. See also https://blogs.bl.uk/digital-scholarship/2021/01/identify-yourself.html.