Moving activities online – as easy as ABC?
By Clive Young, on 10 March 2020
ABC and learning types
As we focus on Teaching continuity, UCL’s ABC method of learning design can help us consider how to move learning activities activities online.
Many colleagues will already be familiar with the ABC sprint workshops for programme and module (re) design. During the high-energy 90’ workshop, academic teams work together to create a visual ‘storyboard’ showing the type and sequence learning activities required to meet the module’s learning outcomes and also how these will be assessed. Over 1000 UCL colleagues have now participated in ABC workshops since we started in 2015 and report it is particularly useful for new programmes or those moving to an online or more blended format.
The storyboard represents the learner journey and is constructed from pre-printed cards representing six types of learning.
The learning types are derived from the highly respected ‘Conversational Framework’ model of adult learning developed by Prof Diana Laurillard of the Institute of Education, UCL.
Video: Prof Laurillard introduces the Conversational Framework (Only the title is in Italian!)
The ABC cards list ‘conventional’ and digital examples activity associated with each of Prof Laurillard’s learning types, but teams are able and encouraged to add their own activities to the cards. Extensive testing at UCL and elsewhere has showed the creative hands-on, analogue format of the workshop stimulates a wide-ranging discussion. This includes the purpose of the course or programme, teaching methods, alternative technologies and assessment methods and above all the student experience. Even if you are not able to organise a ‘full’ ABC learning design event for your team, the cards themselves can help you identify digital alternatives to current activities.
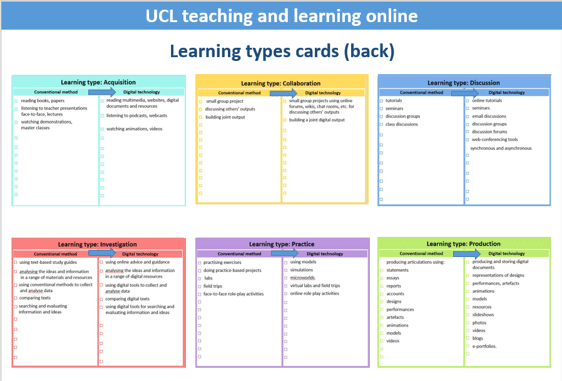
Image: Example activities from the ABC cards.
Video: Prof Laurillard introduces the six learning types (2′) Note: ‘Inquiry’ is used here instead of ‘Investigation’.
How can the six learning types guide us to consider digital alternatives to ‘conventional’ teaching and learning?
![]()
Acquisition
What learners do when they read books and articles, listen to lectures and podcasts, watch demos or videos. In this way learners acquire new concepts, models, vocabulary, models, and methodologies. Acquisition should be reflective as learners align new ideas to their existing knowledge. Conventional methods often include face-to-face presentations, demos and master classes.
Moving acquisition online: reading multimedia, websites, digital documents and resources listening to podcasts, webcasts watching animations, videos. Online quizzes can be used to check learner progress.
Key UCL tools:
- Moodle: Chat, Book, File, Folder, Page, URL (link), Glossary, Lesson, Quiz.
- Lecturecast Universal Capture Personal.
- Blackboard Collaborate.
- UCL Reflect (blog).
- UCL Reading lists.
![]()
Investigation
Encourages the learner to take an active and exploratory approach to learning, to search for and evaluate a range of new information and ideas. Students are guided to analyse, compare and critique the texts, data, documents and resources within the concepts and ideas being taught.
Moving investigation online: in many disciplines using digital resources and analytical tools are already part of students’ activities.
Key UCL tools:
- Moodle: Chat, Database, Forum, Hot Question, Questionnaire, Survey.
- Blackboard Collaborate.
- UCL Reflect (blog).
![]()
Practice
Enables knowledge to be applied in context. The learner modifies actions according to the task and uses feedback to improve. Feedback may come from self-reflection, peers, the teacher, or from the activity outcomes. Practice often includes significant face-to-face components including labs, field trips, placements, practice-based projects and face-to-face role-play and groupwork.
Moving practice online: The most challenging of the six activity types, some activities are hard to substitute without losing important learning outcomes. Videos of methods, simulations, models, sample data sets, image and video banks, online role-play and case studies may be used to address some of the learning aims. Online quizzes can be used to test application and understanding.
Key UCL tools:
- Moodle: Assignment, Assignment (Turnitin), Chat, Database, Forum, Glossary, HotPot, Lesson, Quiz, Wiki, Workshop.
- Blackboard Collaborate.
- UCL Reflect (blog).
![]()
Discussion
Requires the learner to articulate their ideas and questions, and to challenge and respond to the ideas and questions from the teacher, and/or from their peers. Conventionally this is achieved through face-to-face tutorials, seminars and class discussion.
Moving discussion online: There are a number of good online options, including Moodle discussion forums which can be real-time (synchronous) or run over an extended period (asynchronous). Online forums can be even more productive than conventional tutorials as more students may contribute. For a richer discussion, Blackboard Collaborate can be run as a synchronous session.
Key UCL tools:
- Moodle: Chat, Forum, Hot Question.
![]()
Collaboration
Requires students to work together in small groups to achieve a common project goal. Building on investigations and acquisition it is about taking part in the process of knowledge building itself. Learning through collaboration therefore includes elements of discussion, practice, and production.
Moving collaboration online: Some parts of group and project working lend themselves to digital communication to help discussion and planning of project outputs. The practical elements depend on the discipline but in some areas it will be possible to build a joint digital output and complete the task entirely online.
Key UCL tools:
- Moodle: Chat, Forum, Hot Question.
- Blackboard Collaborate.
- UCL Reflect (blog).
![]()
Production
How the teacher motivates the learner to consolidate what they have learned by articulating their current conceptual understanding and reflect how they used it in practice. Production is usually associated with formative and summative assessment and can cover a wide range of items; essays, reports, designs, performances, articles, models etc.
Moving production online: In some disciplines, digital representations are already common such as presentations, videos, slideshows, blogs and e-portfolios.
Key UCL tools:
- Moodle: Assignment, Assignment (Turnitin), Chat, Database, Forum, Glossary, HotPot, Lesson, Quiz, Wiki, Workshop.
- Blackboard Collaborate.
- UCL Reflect (blog).
Assessment
During the ABC workshop, assessment is usually addressed as a part of the (re) design process. Online formative assessment can be included in the learner experience using many of the tools and approaches listed above, such as Moodle Forum and Moodle Quiz. Online summative assessment is more complex and separate guidance is being prepared.
2 Responses to “Moving activities online – as easy as ABC?”
- 1
-
2
Deborah Trayhurn wrote on 11 August 2020:
This is great stuff, many thanks
Do we have any advice for developers around the amount of content / learning loads which might be applied to activities please.
 Close
Close


[…] https://blogs.ucl.ac.uk/abc-ld/moving-activities-online-as-easy-as-abc/ […]